Before starting with the topic, here is a recommended reading for the medical professionals.
Yellowish discoloration of skin and sclera – ” Jaundice” is a commonly encountered problem for the parents of newborn babies. Jaundice is caused by the increase in level of bilirubin in blood (serum). Many parents notice yellowness first in the eyes and then the face and are overly concerned about the problem while the others who have previously parented a baby are convinced that even normal newborn babies developed certain amount of yellowish discoloration. Almost 70% of term babies and 80% of prematurely born babies develop some amount of jaundice but only around 10% of them require medical intervention. This means most are physiological jaundice and is benign in nature.
However, since the consequences of severe jaundice leads to brain damage, it is important to differentiate the physiological from pathological jaundice.
Some Frequently asked questions by Parents
A. When should I be concerned about jaundice?
Certain risk factors increases the chance that jaundice becomes severe needing timely intervention. The absence of these risk factors however does not rule out the chance of developing severe jaundice. Therefore, assessment by a clinician whenever you are concerned about jaundice becomes vital.
- Jaundice developing within 24 hours of birth
- When mother blood group is Rh-ve or O blood group ( Rh and ABO incompatibility)
- Premature babies developing jaundice (< 38 completed weeks gestation babies)
- Signs of underlying illness like vomiting, poor feeding, fever or low tempertature, fast breathing or poor breathing effort.
- Presence of bruises on body, swelling of scalp or blood collection on othersites.
- Intrauterine infections in mother ( TORCH infections)
- Family history of severe jaundice in previous infant
- Persistence of jaundice beyond 3 weeks.
- Passage of white stools.
B. Should I breast feed the baby with jaundice?
Breast feeding should be continued adequately. But in some instances of Breastmilk jaundice if decided by the Doctor, it may need to be switched to formula feed for 48-72 hours. This is decided by your pediatrician.
C. Should mother avoid turmeric or other food if baby has jaundice?
Mother need not abstain from any food. Baby’s jaundice is not related to mothers food but is caused by bilirubin produced in baby’s blood itself.
D. What will Doctor do to check the jaundice?
If the jaundice appears less from clinical visual assessment, doctor will simply advice you to follow up after few days. But it it appears high then he/she will perform some tests.Jaundice can be checked by device from skin with out pricking for blood or by sending blood samples.
E. If jaundice is severe, what are the treatments available?
There are 2 effective treatments.
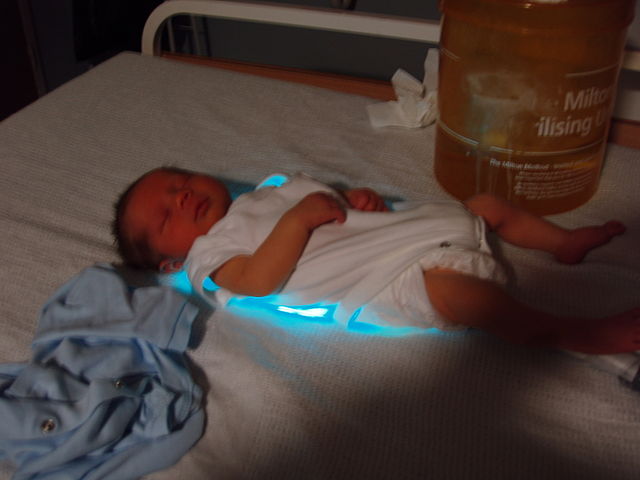
- Phototherapy: Blue/White light therapy under which babies are kept without clothes to decrease the bilirubin in the blood.
- Exchange transfusion: Exchanging the blood of baby with another blood.
Other modalities are drug therapy like Phenobarbitone, etc. that are all decided by doctor in special circumstances.
F. If my jaundiced baby required extensive management, what else will I need to do?
For severe cases, doctor will advice you to perform hearing evaluation on a later date, as high bilirubin can cause hearing defects.
G. What happens if significant jaundice is not treated?
If the level of bilirubin in blood crosses significant level, it may cross the blood brain barrier and affect the brain causing damage. Therefore, whenever a concern of jaundice is there, a visit to a doctor is important and also if the baby has been discharged early from the Hospital, a quicker follow up with in days is required.

MD Pediatrics and Fellowship Neonatology, he chooses to stay anonymous. He often writes his views online as well as share few important topics for medical students, doctors and specially parents. He does research in pediatrics.