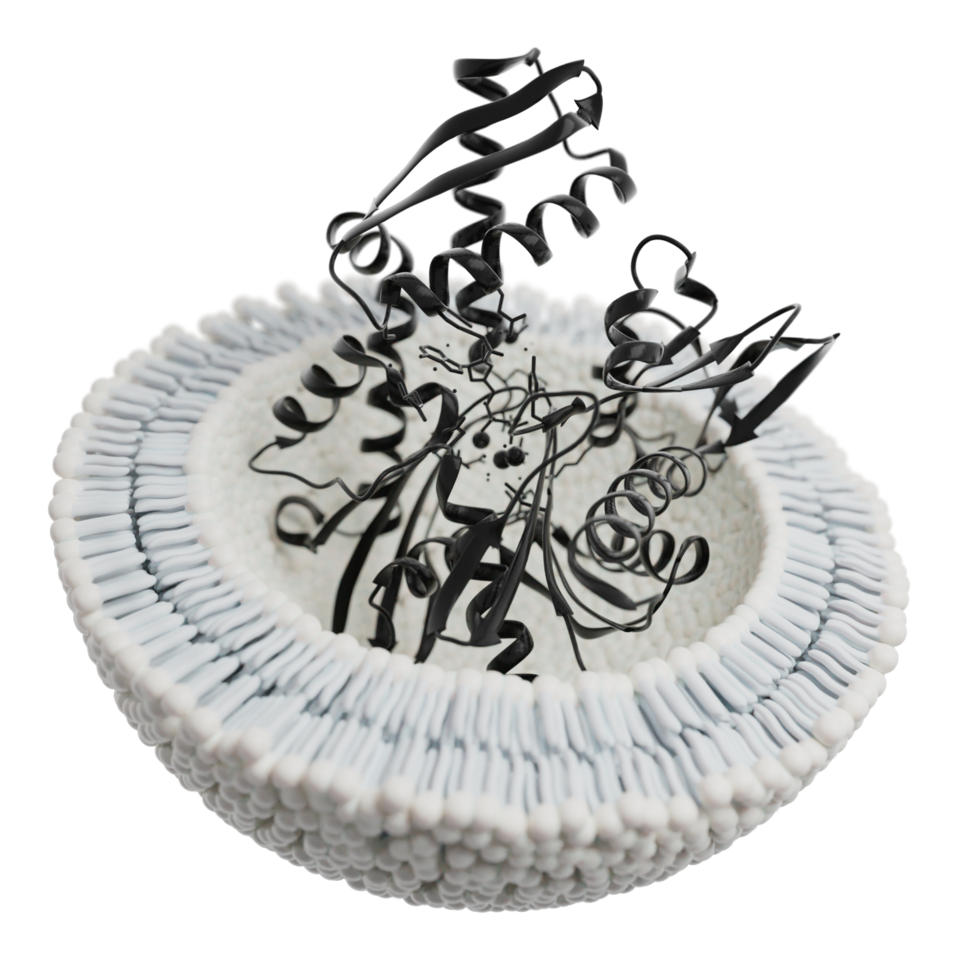
In the realm of regenerative medicine, exosomes are quickly becoming one of the most innovative tools for promoting healing and cellular communication. These nano-sized vesicles are secreted by many cell types, but those originating from mesenchymal stem cells—referred to as stem cell exosomes—are of particular interest for clinical use. Rather than being living cells, exosomes are packets of signaling molecules, such as RNA, DNA fragments, cytokines, and proteins, that influence nearby or distant cells to initiate repair, regulate immune activity, and stimulate regeneration.
Unlike traditional stem cell therapy, which involves transplanting whole cells, exosomes therapy is cell-free, making it a safer and more targeted approach for many patients. Because they do not replicate or carry nuclear material, exosomes avoid many of the complications associated with live cell treatments. Furthermore, their tiny size allows them to circulate easily through tissues and reach areas that may be inaccessible to larger therapeutic agents.
Clinical studies are exploring the effectiveness of stem cell exosomes in treating a wide variety of conditions. Their application spans musculoskeletal injuries, autoimmune disorders, dermatological conditions, and certain neurological diseases. Researchers are particularly excited by their ability to reduce chronic inflammation, promote angiogenesis, and stimulate the body’s innate healing response. In orthopedic medicine, exosomes are being investigated for their potential to help repair cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. In neurology, they are being studied for their capacity to cross the blood-brain barrier and deliver neuroprotective signals to damaged tissue.
What sets exosomes therapy apart is its precision. Instead of replacing damaged tissue directly, exosomes act like messengers, guiding the body’s own cells to respond in specific and beneficial ways. This natural mode of action positions exosomes as a promising adjunct or alternative to existing regenerative methods.
Exosomes Treatment: A Breakthrough in Cell-Free Regenerative Solutions
The concept of exosomes treatment is transforming how clinicians and scientists approach recovery and tissue repair. These biologically active vesicles are collected from cultured stem cells under controlled laboratory conditions, then purified and formulated for clinical use. Because they are devoid of cellular DNA, the risk of adverse immune reactions is minimal, and storage and transportation are simpler than those required for live-cell therapies.
Current uses of exosomes treatment are being explored in fields such as sports medicine, dermatology, aesthetic procedures, and even cardiology. In skin care, exosomes have been used to support collagen production, reduce inflammation, and accelerate wound healing. In patients with joint injuries, exosome-based injections may assist in improving function and reducing discomfort. Meanwhile, early-stage research is evaluating exosomes as potential therapies for neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s and multiple sclerosis.
In the future, exosomes could play a vital role in combination therapies. Scientists are already investigating how to merge exosomes therapy with biomaterials or nanocarriers for improved delivery and therapeutic outcomes. Their compatibility with modern technologies such as 3D bioprinting and tissue scaffolding opens the door for personalized treatment strategies that were once confined to theory.
However, the clinical use of exosomes is still in its early stages. While laboratory and preliminary clinical results are promising, ongoing research is crucial to establish the safest and most effective ways to apply exosomes treatment. Regulatory bodies are developing guidelines to ensure quality, standardization, and ethical use, and responsible institutions such as AMSA Biotech are committed to following these evolving best practices.
Ultimately, stem cell exosomes represent a leap forward in regenerative science. As we continue to unravel the full range of their capabilities, exosomes therapy stands out as a flexible, efficient, and less invasive option for supporting healing and restoring health.