Definition
Definition
External Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is the surgery to connect the mucosal surface of lacrimal sac to the nasal mucosa by removing the intervening bone. It creates a permanent anastomosis between the lacrimal sac and medial meatus of nose.
Prerequisite
Common canaliculi must be patent
Indications of External Dacryocystorhinostomy
- Nasolacrimal duct (NLD) obstruction
- Persistent congenital NLD obstruction unresponsive to previous therapies
- Primary acquired NLD obstruction (PANDO)
- Secondary acquired NLD obstruction (SANDO)
- Benign nasolacrimal sac mass
- Chronic dacryocystitis
- Dacryolith
Contraindications of External Dacryocystorhinostomy
Absolute:
- Atrophic rhinitis
- Malignancy
- Rhinosporiodiosis
Relative:
- Nasal polyp
- Sinusitis
- Bleeding disorders
- Deviated nasal septum
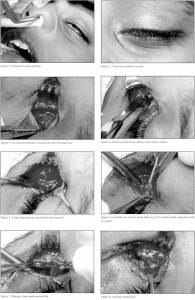
Procedure of External Dacryocystorhinostomy
2. Anesthesia: Peribulbar > General anesthesia > Nerve blocks (Infra-orbital, Infra-trochlear)
3. Skin incision: Curvilinear or straight 10 mm long; 8 mm medial to inner canthus
4. Blunt dissection: Orbicularis oculi, Medial palpebral ligament
5. Anterior lacrimal creast exposed and periosteum elevated
6. Lacrimal sac exposed and dissected away from lacrimal fossa
7. Creation of bony ostium using Kerrison bone punch
- Size: 15 mm X 10 mm
- Removal of anterior lacrimal crest and bones of lacrimal fossa
8. Exposure of thin, pinkish, white nasal mucosa
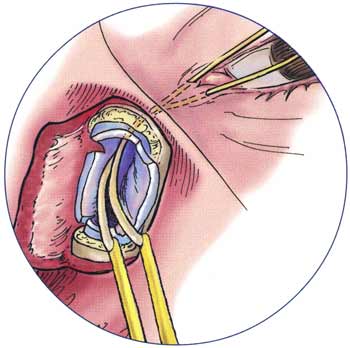
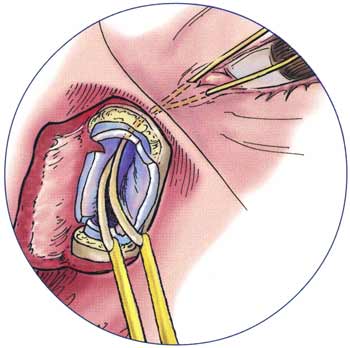
9. Flap formation:
- Sac flaps: Using bowman’s probe as a guide, “H” shaped incision is made with number 11 or 15 blade right across the sac from fundus to the nasolacrimal duct
- Nasal mucosal flaps: Using number 11 blade, “H” shaped incision is made in nasal mucosa along bony ostium
10. Flap anastomosis (Using 6-0 vicryl):
- Posterior flaps of sac and nasal mucosa are sutured
- Anterior flaps of sac and nasal mucosa are sutured
11. Wound closure:
- Medial palpebral ligament and orbicularis with 6-0 vicryl
- Skin with 6-0 silk
Adjunctive measures:
- Mitomycin C 0.04%: If intra-sac synechiae, soft tissue scarring, complicated surgery
- Silicone intubation: All above + Canalicular problems, inadequate flaps
Postoperative measures in External Dacryocystorhinostomy
1st Postoperative day:
- Ice packs to reduce swelling
- Keep head of bed at 30 degrees to reduce swelling
- Nasal pack (if any) is removed and hemostasis is assessed
- Wound is cleaned
- Topical antibiotics on incision site and conjunctival fornix
- Oral antibiotics and analgesics
- Steroids, Nasal decongesants and Steroid nasal sprays
1st Week:
- Change dressing daily or as needed
- Topical antibiotics twice daily
- Oral antibiotics is continued
- Advice not to blow nose to prevent lid emphysema
After 1 week:
- Sutures are removed
- Oral medications are discontinued
- Topical steroids tapered
- Nasal medications X 2 weeks
Follow up:
- At 6 weeks
- At 12 weeks: Tube removal if any
- At 6 months
Complications
Early (1-4 weeks):
- Hemorrhage
- Wound dehiscence/infection
- Tube displacement
- Excessive rhinostomy crusting
- Intranasal synechiae
Intermediate (1-3 months):
- Granulomas at rhinostomy site
- Tube displacement
- Intranasal synechiae
- Punctal cheese-wiring
- Prominent facial scar
- Non-functional DCR
Late (>3 months):
- Rhinostomy fibrosis
- Webbed facial scar
- Medial canthal distortion
- Failed DCR
Comparison with Endoscopic DCR
| Endonasal DCR | External DCR | |
| Scar | No | Yes |
| Bleeding | Less | More |
| Duration | 15-30 minutes | 30-45 minutes |
| Risk of injury to medial canthal structures | Less | More |
| Postoperative morbidity | No | Yes |
| Success rate | 70-90% | 95% |
| Contraindicated in acute infections | No | Yes |
| Skill and expense | More | Less |
Indications of Endonasal DCR:
- Failed external DCR
- Synechiae near opening of fistula
- Inadequate removal of bone
- Common canalicular block
3 Techniques of DCR:
- External DCR
- Endoscopic DCR
- Laser DCR