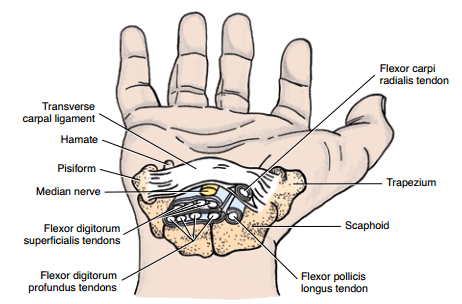
Synonyms: Carpal canal Definition of Carpal Tunnel Carpal tunnel is an osseofibrous space on the palmar aspect of wrist extending from distal volar wrist crease to the mid-palm, which serves as a passageway to the palm for flexor tendons and the median nerve. Boundaries of Carpal Tunnel A. Roof: Flexor…
Tag: Musculoskeletal system
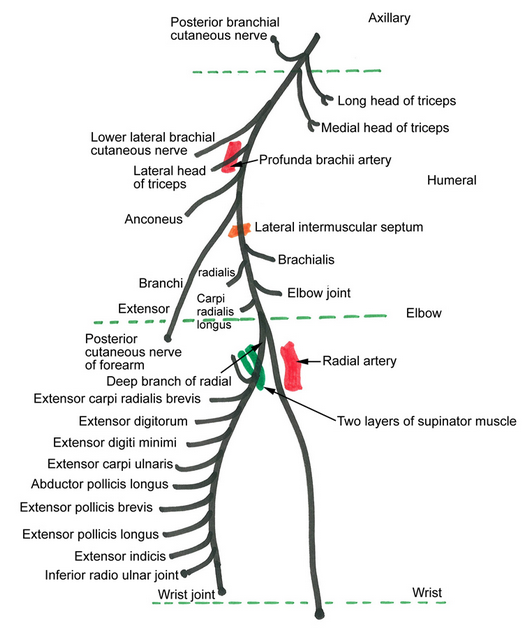
Radial Nerve Anatomy : Course and Innervation
Synonyms: Nervus radialis, Musculospiral nerve Recommended reading: Course 1. Origin: Terminal branch of Posterior cord of brachial plexus (Root value: C5, C6, C7, C8, T1) 2. Posterior axilla: It lies behind the axillary and upper part of the brachial arteries, passing anterior to tendons of subscapularis, lattisimus dorsi and teres…
Applied anatomy of Knee Joint
A. Osteology: 1. Femur: Largest bone in the body Distal femur possess 2 condyles of which the medial one is larger Medial epicondyle is more porminent and supports the adductor tubercle 2. Patella (Knee cap): Largest sesamoid bone Functions: fulcrum for quadriceps protects knee joint enhances lubrication and nutrition of…
Applied anatomy of Anatomical Snuff Box
Synonyms: Radial fossa, Foveola radialis Note: Depression in the humerus which receives the head of radius is also named as Radial fossa Definition: It is a triangular shaped depression in the radial or lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand which is seen when the thumb is extended fully….
Leprosy: Etiopathogenesis, Classification and Complications
Synonyms: Hansen’s disease, Kushta roga, Mezels Definition: Leprosy is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium leprae which affects prinicpally the skin and peripheral nerves. Other commonly affected sites are the cooler parts of the body like mucosa of upper respiratory tract, anterior chamber of eyes and testes. The cooler…
Anatomy and Physiology of Sebaceous glands
Definition: Sebaceous glands are numerous microscopic glands in the dermis that usually open into the hair follicles and secrete sebum. They are holocrine glands, i.e., the sebum consists of the entire secreting cells. Location: Found everywhere on the skin apart from the palms and soles Types of Sebaceous glands: 1….