Choice of Suture: Non-absorbable (braided suture provides slightly superior grip on tubing than monofilament sutures)
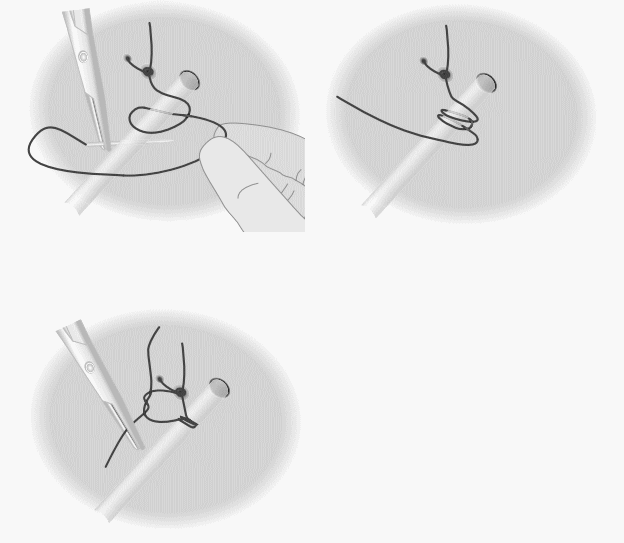
Technique 1:
- Create a series of knots around the drain.
- The long end of the thread (attached to the needle) is passed through the skin directly next to the drain exit site, to create a loop, which is closed using a classic surgical knot.
Further reading: Mura S, Guarneri GF, Parodi PC. A modified technique for securing drains to the skin. JPRAS Open. 2018 Jun 23;17:21-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2018.06.002. PMID: 32158827; PMCID: PMC7061563.
Technique 2: Roman Gaiter Fixation Technique
- Tie suture to the skin, leaving both tails long.
- Wind each end around the tube once and tie again.
- Assistant should hold the tube upwards.
- Threads are wound around tubing, advancing along its length, ~1 mm with each wrap.
- A single throw is placed each time the threads cross (i.e. at each turn).
- Each throw should be tight enough to indent the tubing.
- The tubing should be forced into a slightly tortuous shape; otherwise it is unlikely to have a firm enough grip and liable to slip.
Technique 3: Locking-Turns technique
- Tie a suture to skin, leaving a tail (which will be used later to tie the knot).
- Create multiple locking loops on tube using the needled-end.
- Loops are drawn tight until the tubing is slightly waisted.
- Live (Needle) end is now tied to the other, previously unused, tail of the original skin knot to anchor.
Further reading: Partridge, R., & Sabharwal, A. J. (2013). A31 Drains and Drain Fixation Techniques. Basic Techniques in Pediatric Surgery, 107–109. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-20641-2_31