Indications:
- Monteggia fractures
- Mayo type II olecranon fractures
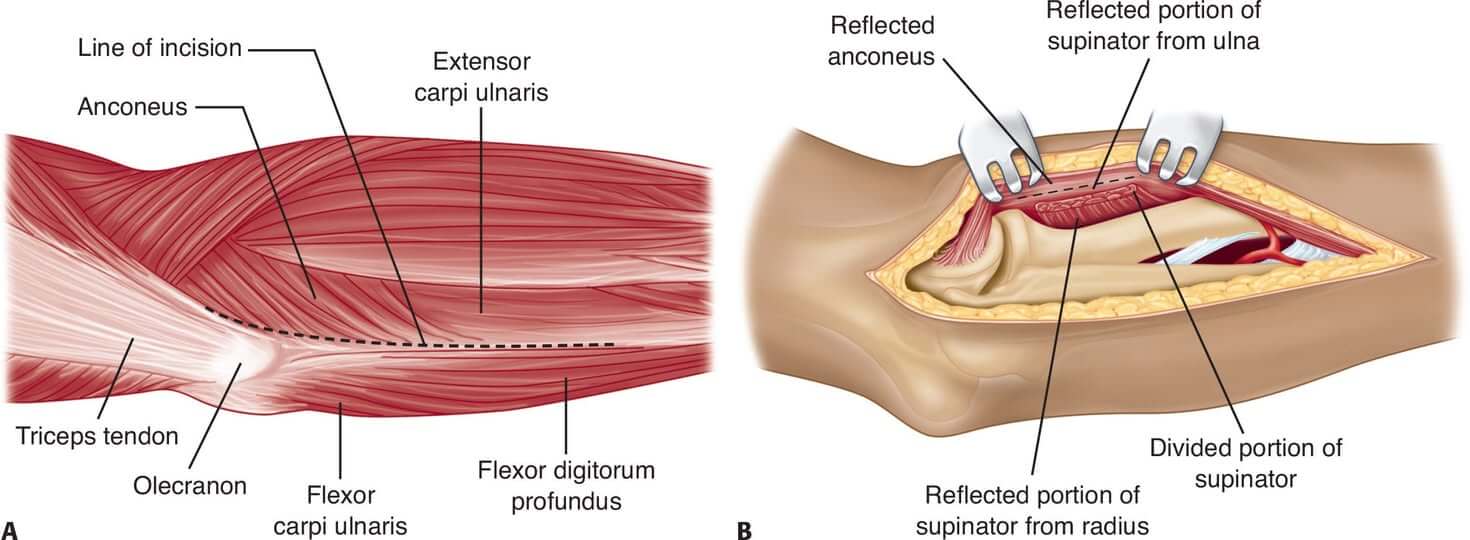
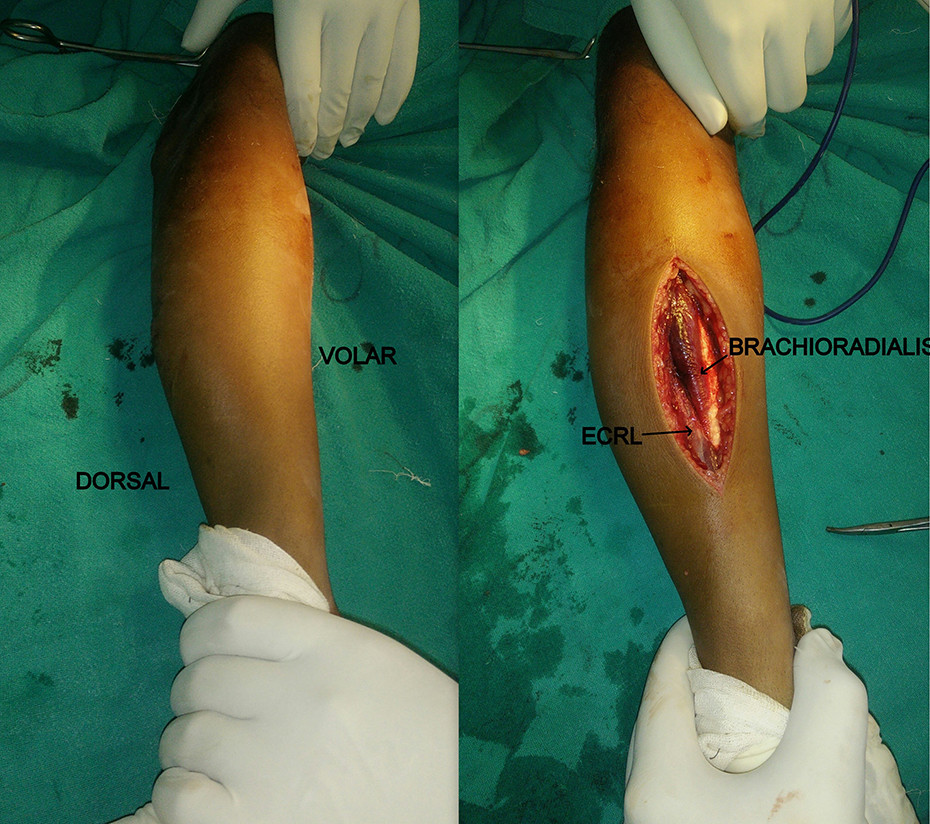
Skin incision: Begin the incision just posterior to the lateral epicondyle and lateral to the triceps tendon, and continue the incision distally to the lateral tip of the olecranon and then down the subcutaneous border of the ulna to the junction of its proximal and middle thirds or as necessary
Superficial dissection: Incise the deep fascia in line with the incision to approach the lateral margin of the ulna between the anconeus insertion and the flexor carpi ulnaris.
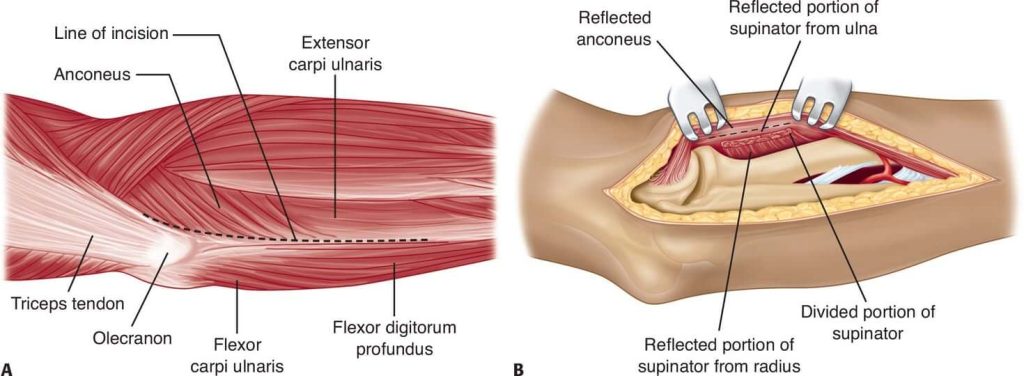
Deep dissection: The anconeus and extensor carpi ulnaris are stripped subperiosteally from the ulna, beginning on the lateral subcutaneous crest of the bone and reflecting the muscles volar-ward. The supinator is released subperiosteally from its ulnar insertion, and the entire muscle mass is reflected anteriorly.
Deep to this layer, the annular ligament, the lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL), and the joint capsule complex are identified. The radial head can be palpated deep to these. Attention should be paid to the insertion sites of these structures for later reference when performing an anatomic repair. The ligaments and capsule are released directly off the ulna at the supinator crest using sharp dissection.
Further reading:
- Speed and Boyd’s approach to the forearm shaft
- Posterolateral (Boyd) approach to the pediatric proximal radius and ulna
- Versatility Through the Boyd Approach – Eric G. Huish, Jr, DO and Marc A. Trzeciak, DO