Tension Band Principle
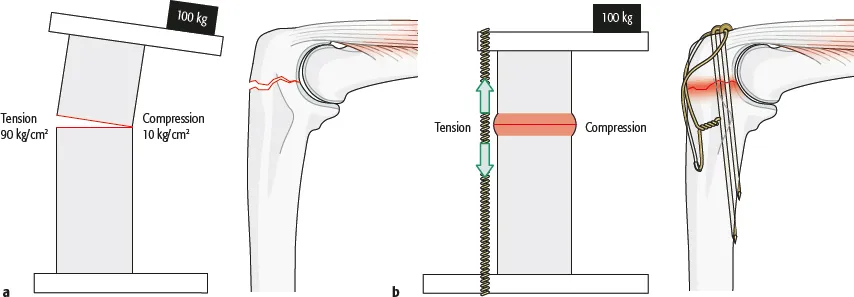
A tension band is any device placed on the tension side of an eccentrically loaded fracture that converts tensile load into compressive load. The convex side of the bone is under tension whereas the concave side is under compression.
For a tension band to work, the fracture site must be eccentrically loaded. In addition, the construct must withstand compressive forces on the compression side, i.e. the compression cortex must be stable.
Pre-requisites
- Good bone quality (able to withstand compression)
- Intact cortical buttress on compression side
Types
1. Static
- Compression remains fairly constant during movement of nearby joints
- Example: Tension band wiring of medial malleolus fracture
2. Dynamic
- Compression force tends to increase with movement of nearby joints
- Example: Tension band wiring of patella, greater trochanter, olecranon, greater tuberosity of humerus
References:
- tension band principles (aofoundation.org)
- Orthopedics and Trauma – Principles and Practice, 2nd Edition (MN Kumar)