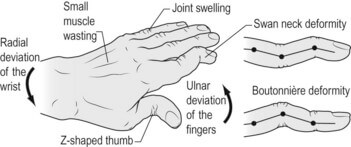
Alterations in the relationships between the balanced extrinsic and intrinsic musculature of the hand due to trauma or secondary to the effects of systemic disease may cause the development of functional deformities such as a boutonnière or swan-neck deformity.
| Swan-neck deformity | Boutonniere deformity | |||
| Deformity | PIPJ | Hyperextension | PIPJ | Flexion |
| DIPJ | Flexion | DIPJ | Hyperextension | |
| MCPJ | Flexion | MCPJ | Extension | |
| Thumb | Not affected | May be affected | ||
| Function | Impaired | Inability to make fist due to PIPJ hyperextension | More of aesthetic concern | Able to make fists |
| Causes and Biomechanics | Wrist synovitis | Carpal collapse, supination and ulnar translation lengthens/weakens extrinsic tendons which are then overpowered by intrinsic tendons resulting in MCPJ flexion and PIPJ extension | Central slip dysfunction from tear (trauma) or attenuation (synovitis in RA) | Triangular ligament stretches |
| MCPJ synovitis | Weakened extensor tendon insertion at P1 increases extensor force on P2 leading to PIPJ hyperextension | Lateral bands sublux in volar direction maintaining a persistent PIPJ flexion | ||
| MCPJ volar plate | Weakened volar plate leads to MCPJ subluxation and shortened intrinsics which causes PIPJ hyperextension | Concentration of extensor force on DIPJ | ||
| PIPJ synovitis | Attenuates volar plate and triangular retinacular ligament (TRL) resulting in dorsal translation of lateral band and destruction of FDS insertion leading to PIPJ hyperextension and DIPJ flexion due to increase in FDP tension and decrease in lateral band tension | In chronic cases, fixed contracture develops | ||
| PIPJ volar plate | Lax volar plate allows for PIPJ hyperextension | |||
| DIPJ mallet injury | Extensor power is concentrated on the central slip resulting in PIPJ hyperextension and volar plate weakens over time | |||
| Classification and management | Nalebuff’s | Nalebuff and Miller’s | ||
| 1 | Flexible | 1. PIPJ extension block splints (Figure of 8 or Murphy ring) 2. FDS sling/tenodesis i.e. Beckenbaugh technique (FDS slip is transected and brought over A2 pulley and sutured back to itself) 3. Littler ORL reconstruction (creation of ORL using lateral band) 4. Lateral band mobilization and skin release (Nalebuff and Millender) | Extensor lag of 10-15 degrees, passively correctable | 1. Splinting (DIP in full extension) 2. Dolphin or Folwer tenotomy (Releasing lateral tendons near their insertion into distal phalanx) |
| 2 | Intrinsic tightness | Intrinsic release at MCPJ | Extensor lag of 30-40 degrees, passively correctable | Shorten central slip or Centralize lateral bands |
| 3 | Fixed hyperextension deformity of PIP | 1. MUA 2. Intrinsic release | Fixed flexion deformity with retinacular tightness (ORL and TRL) | ORL (which maintains DIP extension and prevents flexion) stretching and then proceed as in stage 2 when PIP is fully extended |
| 4 | Arthritic | 1. Arthrodesis of PIPJ 2. Arthroplasty | Arthritic | Arthrodesis or Swanson type arthroplasty |
Acronyms used:
- MCPJ: Metacarpophalangeal joint
- PIPJ: Proximal interphalangeal joint
- DIPJ: Distal interphalangeal joint
- TRL: Triangular retinacular ligament
- ORL: Oblique retinacular ligament
- P1: Proximal phalanx
- P2: Middle phalanx
- FDS: Flexor digitorum superficialis
- MUA: Manipulation under anesthesia