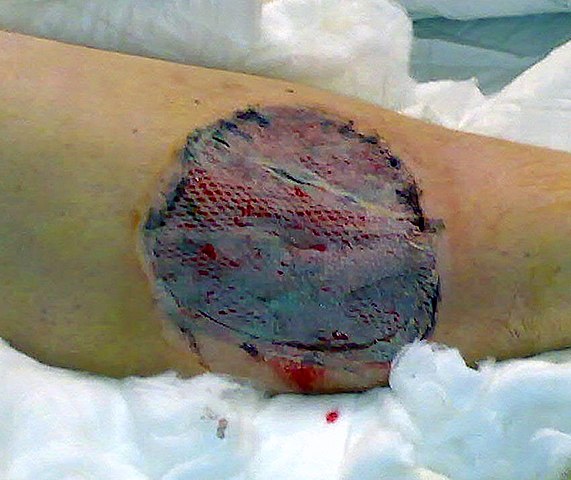
Mnemonic: AIIRR
I – Adherence
- Formation of fibrin bonds between graft and it’s recipient wound bed
II – Imbibition (1st 2-4 days)
- Donor tissue receives nutrition from absorption from the recipient site wound bed via capillary action (graft drinks from recipient bed)
- Graft increases in weight and volume and appears white
Bleeding, infection and mechanical movement due to improper immobilization of the area can lead to graft failure at this stage.
III – Inosculation and Revascularization (Over following 3-4 days)
- Inosculation: Direct anastomosis between the vessels in the bed and those in the graft (graft begins to look pink)
- Revascularization: New vessel ingrowth from the bed along the vascular channels of the graft
- Neovascularization: New vessel ingrowth from the bed along the new channels in the graft
Insufficient vascular proliferation, development of thick layer of fibrin or hematoma or seroma can lead to failure of graft uptake in this stage. Hence, compression is useful.
IV – Remodelling (>7 days)
- Fibrin adhesion between graft and recipient bed is replaced by fibroblast (securely adherent to bed by 10-14 days)
- Changes to the histological architecture of the graft to return to its original form
- Lymphatic drainage by day 6
- Collagen replacement from day 7 to week 6
- Vascular remodeling for months
- Re-innervation and regeneration of dermal appendages
Contracture:
– More the dermal component in graft, less the contraction
– Recipient bed contracts as well
– These may lead to achromic fissures and perigraft halo (overlapping of the graft edges at the recipient site can prevent these complications)
References:
- Textbook on Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery By Mysore Venkataram
- Burns (OSH Surgery) edited by Iain S. Whitaker, Kayvan Shokrollahi, William A. Dickson