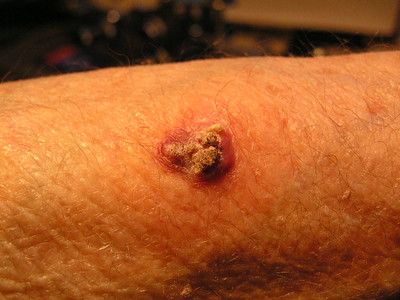
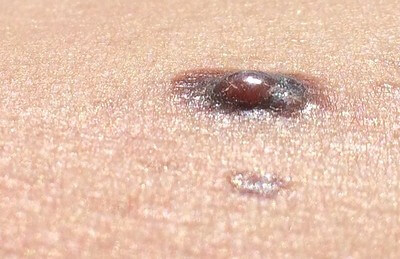
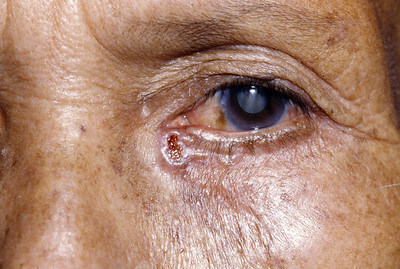
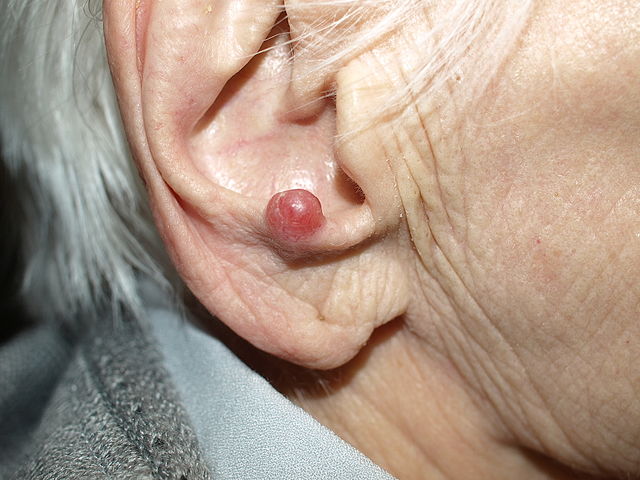
Malignant Melanoma
Diagnosis or Clinical features:
Mnemonic: ABCDE
- Asymmetric with non-matching sides
- Borders are irregular
- Color is not uniform (variegated)
- Diameter >6 mm (pencil eraser)
- Evolving lesions (size, shape, surface, color, symptoms)
Risk factors:
Mnemonic: MM RISK
- Moles: atypical nevus (>5)
- Moles: common moles (>50)
- Red hair and/or freckling
- Inability to tan (skin types I and II)
- Sunburn history (severe sunburn before age 14)
- Kindred (family history of melanoma)
Pathologic Types:
Mnemonic: Melanoma Always Spreads to Nodes (in order of worsening prognosis)
| Mnemonic | Type | Incidence | Site | Growth pattern |
| Melanoma | Maligna – lentiginous | 10-15% | Face (Precursor – Hutchison’s freckles/lentigo maligna) | long in-situ stage before vertical growth |
| Always | Acral lentiginous | 30-70% dark skinned (most common in dark skinned) 5% fair skinned | Palm, soles, nail beds Hutchison’s sign – extension of acral lentiginous melanoma to nail folds | |
| Spreads to | Superficial spreading | 50% (most common) | Trunks (male), legs (female) | grows radially before vertically |
| Nodes | Nodular | 15% (5% are amelanocytic) | Trunks & legs | only vertically |
Clarke’s level: Anatomical measure of tumor depth –
Mnemonic for layers of skin: E-D-F; Dermis has 2 layers (P comes before R)
- Epidermis (level I; best porgnosis)
- Dermis – Papillary (level II)
- Dermis – Papillary and Reticular junction (level III)
- Dermis – Reticular (level IV)
- Fat (level V; worst prognosis – 75% chance of 5-year recurrence)
Breslow’s thickness: the depth of invasion from the stratum granulosum
| Stage | Breslow thickness | 5-year survival | Resection margin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insitu | Insitu | 90-100% | 0.5 cm |
| I | <1 mm | 80-90% | 1 cm |
| II | 1-2 mm | 70-80% | 1-2 cm |
| III | 2-4 mm | 60-70% | 2-3 cm |
| IV | >4 mm | 50% | 3 cm |
If ≥ Clarke level IV, thickness >1 mm or ulceration: consider Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB) and possible lymphadenectomy.
Malignant MElanoma is more likely to MEtastasize.
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
It is the most common skin cancer.
Mnemonic: B’s and P’s
Involvement: Basal cell layer of epidermis
Risk factors:
- uvB
- Basal cell nevus syndrome (Gorlin syndrome)
- Bazex syndrome (acral psoriasiform dermatosis associated with internal malignancies)
- xeroderma Pigmentosum
- Pale skin (Fitzpatrick type 1 and 2)
- Previous skin cancer
- Poor immune system
Site: uPPer lip or above
Histology: Peripheral Palisading
Clinical features:
Mnemonic: TURP
- Telangiectasia
- Ulceration
- Rolled edges
- Pearly papule
Types:
Mnemonic: MNoPSS
- Morphoeic: Scar like
- Nodular: most common, pearly papule
- Pigmented: Melanoma like
- Superficial: Multifocal
- SCC mixed (Baso-squamous): More aggressive
Treatment options:
| Medical | Surgical |
| Chemotherapy e.g. 5-FU cream | Curettage & Cautery |
| Cryotherapy | Surgical excision |
| Phototherapy | Moh’s micrographic surgery |
| Radiotherapy |
| BCC | Type | Excision margins |
| Primary | Small (<2 cm) | 3 mm = 85% clearance 4-5 mm = 95% clearance |
| Large (>2 cm) or Morpheic | 5 mm = 85% clearance 13-15 mm = 95% clearance Consider Moh’s micrographic surgery (sequential horizontal tumor excision with immediate frozen section examination until clear margins are achieved) | |
| Recurrent | 5-10 mm Consider Moh’s micrographic surgery +/- Radiotherapy | |
| Incomplete excision | Re-excision Consider surveillance |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Involvement: Squamous keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum
Risk factors: Like in BCC
- However, SCC is the most common skin cancer in brown & black skin (Fitzpatrick type 5 and 6)
Premalignant conditions:
Mnemonic: ABC
- Actinic keratosis (10-15% progress to SCC)
- Bowen’s disease (SCC in-situ; 5% progress to SCC)
- Cheek mucosa white that cannot be brushed off (Leukoplakia; 15% progress to SCC)
Clinical features:
Mnemonic: NO SUN
- Nodular
- Opaque
- Sun-exposed areas
- Ulcerating
- Non-distinct borders
Management:
| SCC | Excision margins |
| <2 cm | 4 mm = 95% cure |
| >2 cm | >5 mm = 95% cure Consider Moh’s micrographic surgery |
Merkel cell carcinoma
Mnemonic: AEIOU
- Asymptomatic/lack of pain
- Expanding rapidly (≤ 3 months)
- Immunosuppression (HIV, CLL, Organ transplant, Polyomavirus)
- Older than age 50
- Ultraviolet light skin exposed
Management:
Lesion <2 cm: Excision with 1 cm margin
Lesion 2 cm or more: Excision with 2 cm margin
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB) Positive: Complete Lymph Node Dissection + Radiotherapy
Metastases: Chemotherapy + Radiotherapy