Mnemonic: Remember “S” for Scheurmann
Structural kyphosis (sagittal deformity) of thoracic or thoracolumbar spine
Skeletally immature sons (0.4-10% of adolescents between 10-14 years; onset with prepubertal growth spurt; M:F = 2-7:1)
Strong hereditary (genetic) predisposition and Several theories:
- Scheurmann’s vertebral epiphyseal disturbance theory
- Schmorl’s nodes (herniation of disc material into vertebral body)
- Structural weakness in vertebral body due to persistence of anterior vascular grooves (Ferguson)
- Secondary to juvenile vertebral osteoporosis (Bradford)
- Structural biochemical abnormality of collagen and matrix of vertebral endplates (Ippolito and Ponseti)
Slouching stance (poor posture) and Subacute thoracic pain
Sharp accentuated curve in forward bending test (in contrast to smooth curve in postural kyphosis)
Stiff (rigid) kyphosis (not easily corrected with postural changes or passive manipulation; no correction on hyperextension radiographs)
Spondylolysis, Scoliosis, Skin pigmentation at the apex of kyphosis (Stagnara et.al.), Spinal cord compression (rare)
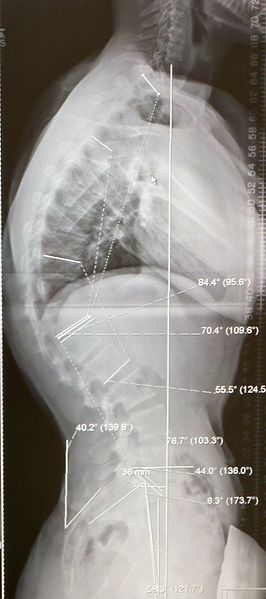
Sorensen’s radiographic criteria for classical/typical Scheurmann’s disease (thoracic commonly):
- Kyphosis of 40 degrees AND
- Vertebral wedging of 5 degrees over atleast 3 consecutive vertebral levels
Scheurmann’s vertebral end-plate irregularities, Schmorl’s node and Space (disc space) narrowing with or without Sorensen’s radiographic criteria in atypical Scheurmann’s disease (thoracolumbar or lumbar commonly).
Subtractive (negative) Sagittal balance (distance measured from sacral promontory to plumb line dropped from center of C7 vertebral body; normal is +/- 2 cm)
Skeletal maturity assessment (Sander’s maturity scale or Risser stage)
Stretching and physiotherapy for less than Sixty degree (<60) kyphosis without Symptoms
Spinal fusion for more than Seventy five (>75) degree kyphosis, Spinal cord compression and Severe refractory pain (Bracing for everything else)