Synonym: Rifampin
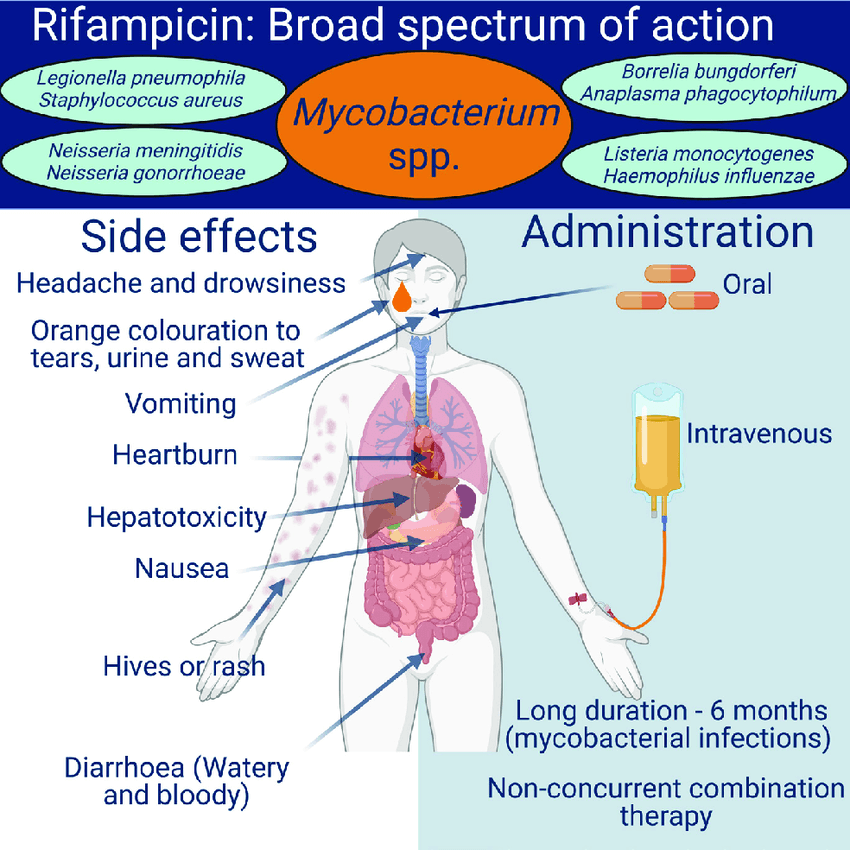
Mnemonic: RIFAMPIN
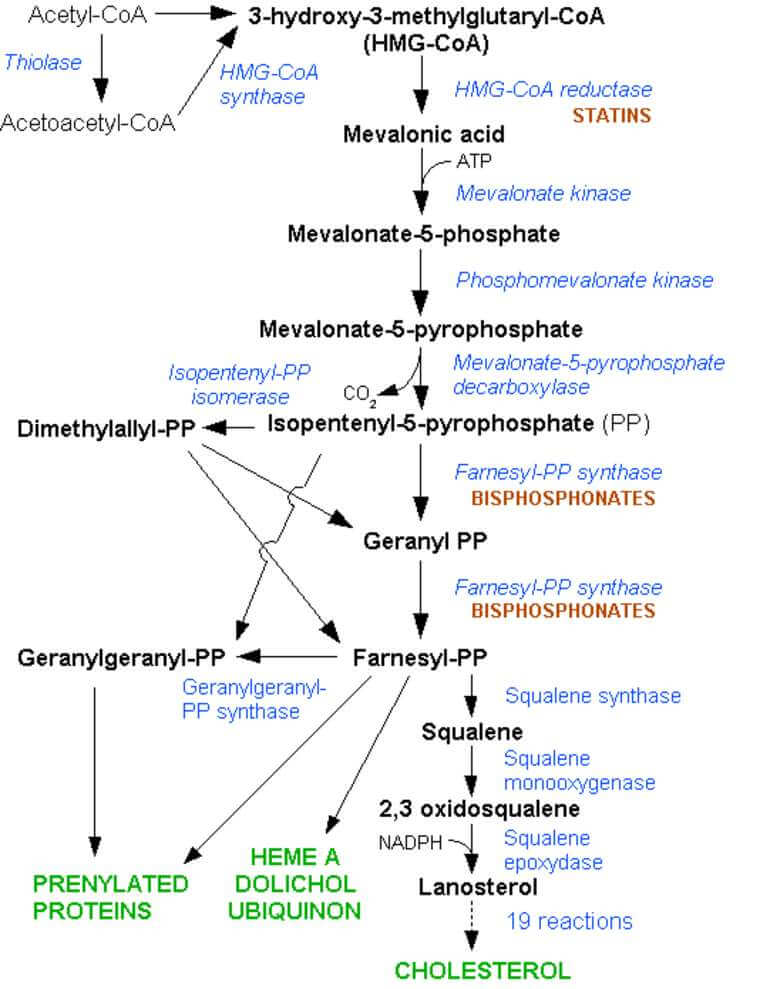
R: RNA polymerase inhibition
- blocks the DNA dependent RNA polymerase leading to RNA synthesis inhibition
- Antimicrobial Mechanism of Actions – Everything you need to know
I: Induces CYP450
- Increases the metabolism of other drugs (Warfarin, OCP, Protease inhibitors) rendering them less effective
F: Flu-like symptoms, Fluid (sweat, urine, tears, saliva) discoloration
A: AST/ALT elevation (Hepatotoxicity is a possible complication)
- Check bloods at baseline and then at two and six weeks after starting and eight weekly thereafter as a minimum.
M: Mycobacteria (M. Tuberculosis, M. Leprae, MAI treatment) and Meningitis (N. Meningitidis prophylaxis for close contacts)
P: Penetrates granuloma, biofilm and blood-brain-barrier, Prosthetic joint infection (one of the clinical uses of rifampicin along with other anti-staphylococcal drugs as it penetrates bio-film)
I: Intestinal problems like nausea/vomiting (most common side effect)
N: Nephritis (Acute interstitial nephritis is a possible complication)
Reference: How to monitor Rifampicin – a brief primer