Mnemonic: Imagine a letter “Z“.
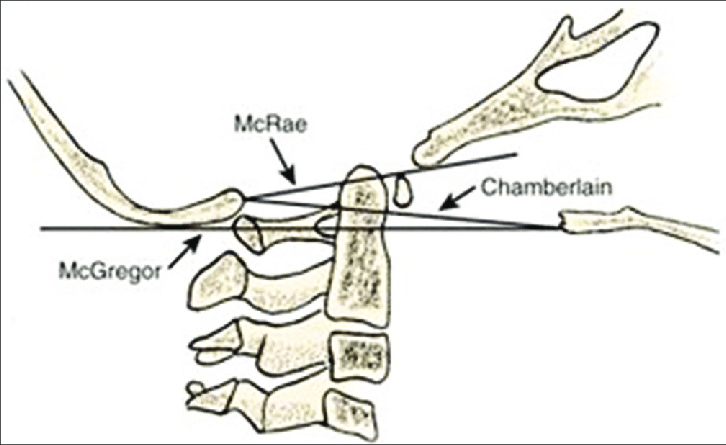
a. McRae’s line has “R” and is at Roof.
b. Chamberlain’s line starts with “C” and is at Center.
c. McGregor’s line has “G” and is at Ground.
a. McRae’s line (foramen magnum line): drawn from anterior margin of foramen (basion) to posterior margin of foramen (opisthion)
- Normal: Tip of dens should not cross this line
b. Chamberlain’s line: drawn from posterior end of hard palate to posterior margin of foramen (opisthion)
- Normal: Tip of dens is no more than 3 mm above this line
c. McGregor’s line: drawn from posterior end of hard palate to posterior occiput curve
- Normal: Tip of dens is no more than 4.5 mm above this line
Other lines
a. Wackenheim’s line (Clivus canal line): Line drawn along clivus into cervical canal
- Normal: Tip of dens is ventral and tangential to this line
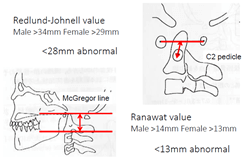
b. Ranawat’s line: A perpendicular line drawn from center of C2 pedicle towards a line from center of anterior to posterior arch of C1
- Abnormal: <13 mm
c. Redlund-Johnell’s method: Measure distance between midpoint of C2 body inferior margin and McGregor’s line
- Abnormal: <28 mm