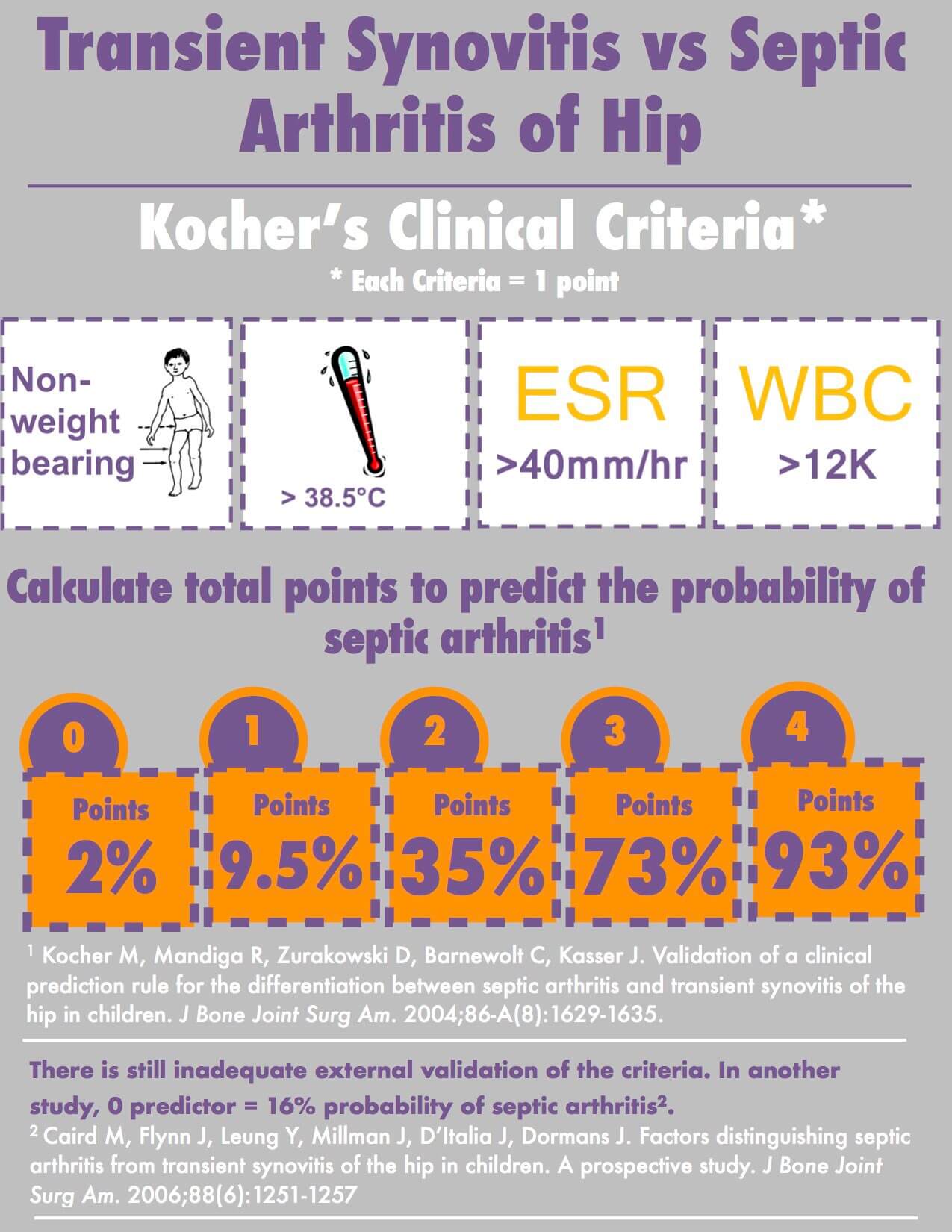
Kocher criteria can help to differentiate between spetic arthritis and transient synovitis in a case of non-traumatic painful hip in a child.
A restrospective study in 104 pediatric patients has depicted that meeting 3 out of 4 crtieria would miss 52% cases and is of limited usefulness in detecting septic arthritis of knee in pediatric population. 1
Another study has demonstrated the limited utility of Kocher criteria in the adult population. 2
Mnemonic for Kocher Criteria: Walk FEW
1. Walking or weight bearing inability
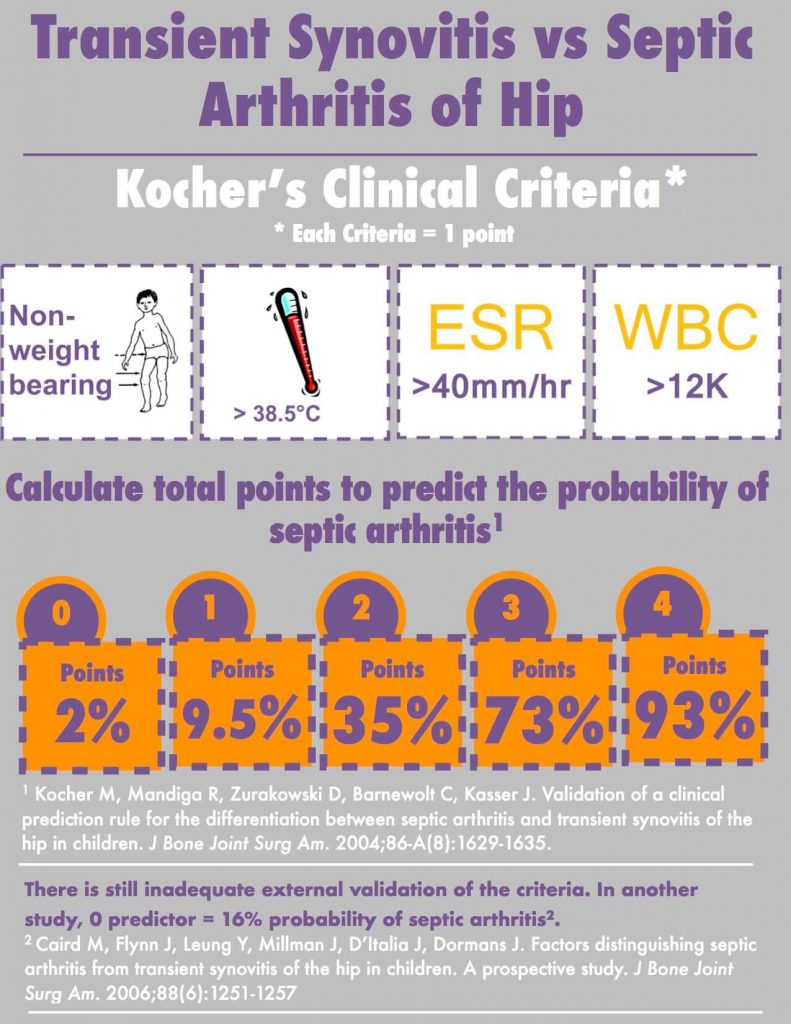
2. Fever > 101.3°F or > 38.5°c
3. ESR >40 mm/hr
4. WBC >12,000/cu.mm
Probability of septic arthritis with number of criterion met:
- 4 out of 4: 99%
- 3 out of 4: 93 %
- 2 out of 4: 40%
- 1 out of 4: 3%
- 0 out of 4: 0.2%
Caird et.al. (2006) added CRP to the Kocher criteria. CRP ≥ 20 mg/L is another predictor of septic arthritis. The best predictor of septic arthritis is fever followed closely by raised CRP. A study by Walker et.al. revealed that an elevated CRP (2.0mg/dL) and inability to bear weight together resulted in a PPV of 78%. With a CRP threshold of 3.0mg/dL and inability to bear weight, the PPV was 81%. 3
The modified Kocher criteria can be easily remembered using the mnemonic: WAIT
1. WBC
2. Acute phase reactants: ESR and CRP
3. Inability to walk
4. Temperature