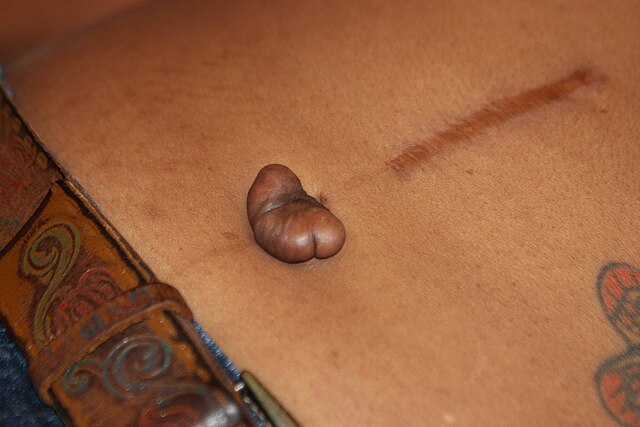
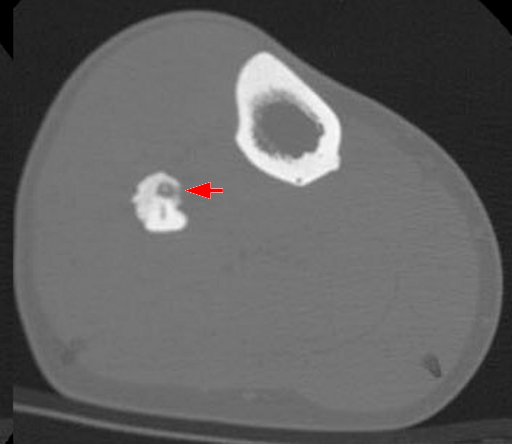
Hypertrophic scars and keloids are both raised, firm scars formed from excess fibrinogen production and collagen during healing.
Mnemonic: BAD SCARS
| Mnemonic | Basis | Hypertrophic scar | Keloid |
| B | Behavior | Natural regression | No spontaneous regressio |
| A | Acuteness | Appears in weeks | Appears over months to years |
| D | Demographic | All races affected | More prevalent in Asian/Afro-Caribbean races Positive family history |
| S | Symptoms | Itch (mast cells) | Itch, Pain, Sensitivity |
| C | Collagen | 3X increased production Type III collagen Well organized Parallel to epidermis With myofibroblasts | 20X increased production Type I + Type III collagen Poorly organized Random to epidermis Without myofibroblasts |
| A | Area | Remains within wound borders | Extends beyond wound borders |
| R | Recurrence | No | Yes |
| S | Site | Extensor surfaces Skin creases | Earlobe Chin Neck Shoulder Chest Deltoid regions Knees |
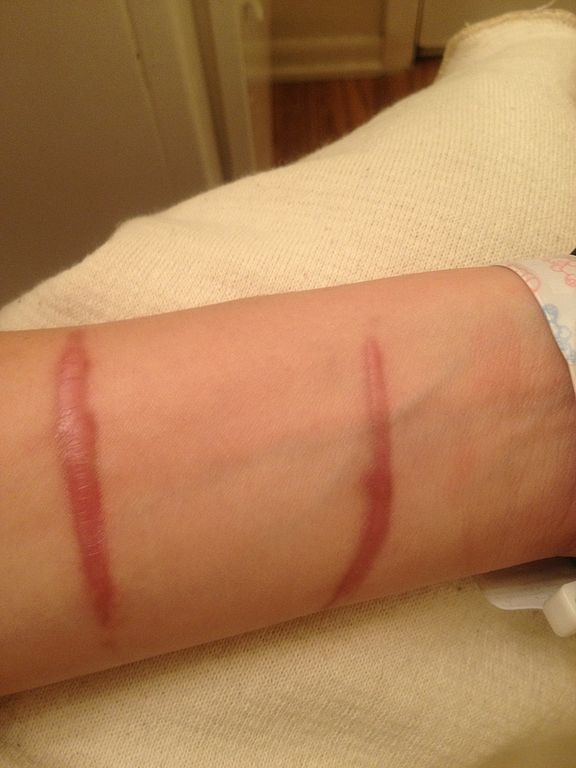
User:Cgomez447, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Management
| Modality | Indication | Comments |
| Occlusive dressing | Hypertrophic scar & Keloid | ↓ delivery of blood, oxygen & nutrients to scar → ↓ collagen synthesis 23 hours/day Works best immediately after surgery/injury |
| Compression therapy | Hypertrophic scar & Keloid | Thinning effect on the skin and reduces the cohesiveness of the collagen fibers |
| Intralesional steroids | Hypertrophic scar & Keloid | Every 4-6 weeks for several months |
| Surgical excision | Hypertrophic scar & Keloid | Ensure tension-free primary closure |
| Radiation | Recurrent Keloid | Begun the day after surgical excision |
| Newer adjuvant & emerging therapies | Interferon, 5-FU, Imiquimod, Tacrolimus, Bleomycin, Retinoic acid, Botulinum toxin A |