New Criteria for HRS
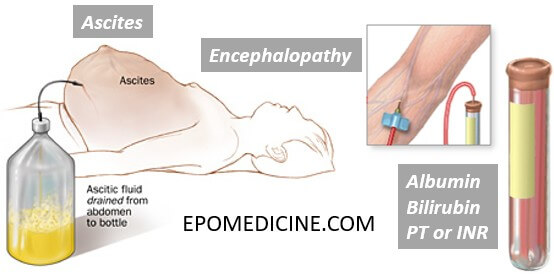
1. Cirrhosis with ascites
2. Serum creatinine >1.5mg/dl
3. No sustained improvement in renal function after 2 days of diuretic withdrawl (if on diuretics) and volume expansion with albumin infusion at 1 gm/kg/day upto a maximum of 100 gm/day.
4. No evidence of shock
5. No nephrotoxic drugs
6. No evidence of parenchymal kidney disease
- Proteinuria <0.5 gm/day
- No microhematuria (RBC <50/hpf)
- Normal renal ultrasonography
Types of HRS
Type 1 HRS
- Rapid and progressive impairment in renal function (increase in serum creatinine of ≥100% compared to baseline to a level higher than 2.5mg/dl in <2 weeks)
Type 2 HRS
- Stable or less progressive impairment in renal function
- Type 2 HRS may convert to Type 1 HRS spontaenously or following precipitating event such as SBP.
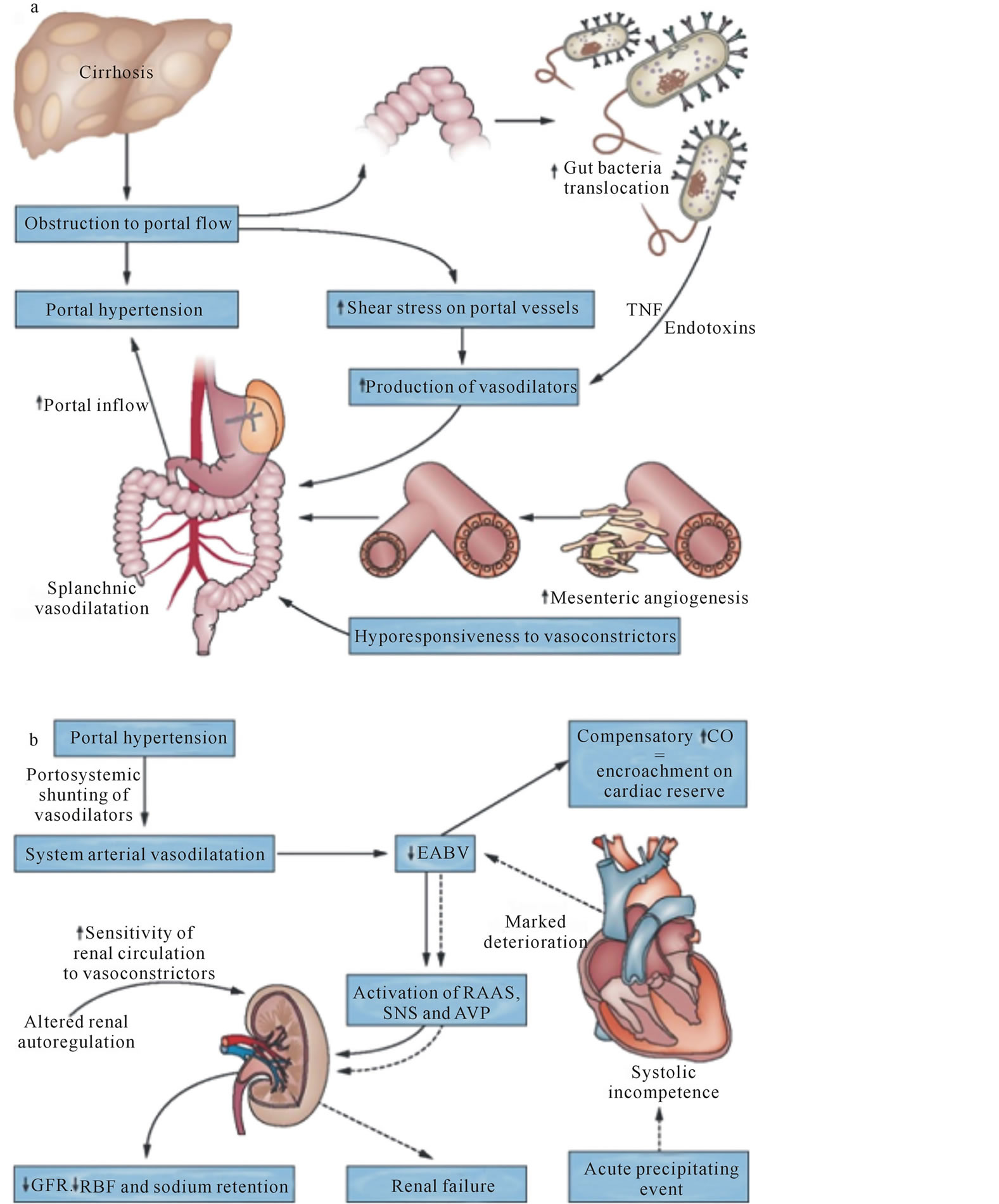
Pathophysiology of HRS
- Splanchnic vasodilation
- Activation of sympathetic nervous system and renal-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS)
- Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy
- Increased vasoactive mediators – LTs, TXA2, endothelins, etc.
Spontaenous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is the most important risk factor for HRS. 30% patients with SBP may go in HRS.
Prevention of SBP
1. Diuretics: concentrates ascitic fluid raising the opsonic activity of asicitic fluid.
2. Infection treatment: early recognition and treatment of localized infection like cystitis and cellulitis.
3. Restrict proton pump inhibitor: PPI facilitate enteric colonization, overgrowth and translocation into peritoneum.
4. Antibiotic prophylaxis: 1
- Indications:
- Cirrhosis with gastrointestinal bleeding
- One or more episode of SBP
- Ascitic fluid protein <1 gm/dl during hospitalization (US recommendation)
- Cirrhosis and ascitic fluid protein <1.5 gm/dl with impaired renal function (creatinine ≥1.2 mg/dl, BUN ≥25 mg/dl or Na+ ≤130 mEq/l) or liver failure (Child pugh score ≥9 and bilirubin ≥3 mg/dl)
- Choice of antibiotics for prophylaxis:
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (one double strength tabled once daily) OR
- Ciprofloxacin 500 mg/day OR
- Norfloxacin 400 mg/day
- Duration of prophylaxis:
- For 7 days in patients with cirrhosis and GI bleeding
- Until hospitalization for patients with ascitic fluid protein <1 gm/dl during hospitalization
- For other conditions – continue until ascites disappears or decompensated liver disease improves
Management of HRS
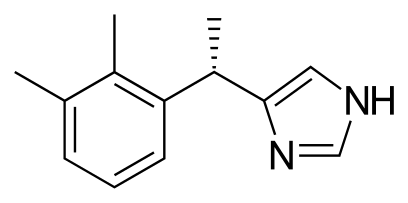
- Terlipressin (vasoconstrictor): 1-2 mg IV every 4-6 hours
- Albumin: 1 gm/kg (to 100 mg) on day 1 then 20-40 mg daily
- TIPPS: if response is suboptimal
- Liver transplant: Optimal
Reference: EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines