GRACE Score
Mnemonic: GRACE
A. Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events
B. Renal: Creatinine
C. Age
D. Cardiac:
- Heart rate
- Systolic blood pressure
- Cardiac arrest at admission
- Killip class:
- I – No CHF
- II – Basal rales and/or JVD
- III – Pulmonary edema
- IV – Cardiogenic shock
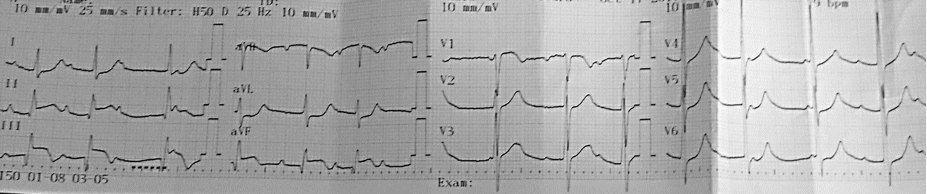
E. ECG and Enzyme:
- ST segement deviation on ECG
- Abnormal cardiac enzymes
For GRACE 6 month risk score:
2 varibales are not used:
- Killip class
- Cardiac arrest at admission
3 other variables are used:
- History of congestive heart failure
- History of myocardial infarction
- No in-hospital PCI
HEART score
Mnemonic: HEART
a. History:
- 2: Highly suggestive of cardiac origins
- 1: Moderately suspicious
- 0: Slightly suspicious
b. ECG:
- 2: Significant ST depression
- 1: Non-specific repolarization differences
- 0: Normal
c. Age:
- 2: >65 years
- 1: 45-65 years
- 0: <45 years
d. Risk factors:
- 2: 3 or more risk factors or history of atherosclerotic disease
- 1: 1-2 risk factors
- 0: No known risk factors
e. Troponin:
- 2: >3 x normal limit
- 1: 1-3 x normal limit
- 0: Within normal limit
Interpretation:
HEART score <4: Low risk (0.9-1.7%) of Major Adverse Cardiac Events (MACE) at 6 weeks (Can be considered for direct ED discharge or early discharge)
HEART score 4-6: Moderate risk (12-16.6%) of MACE at 6 weeks (Recommend admission for medical optimization and further workup)
HEART score >6: High tisk (50-65%) of MACE at 6 weeks (Recommend advancing for early coronary angiogram)
TIMI Score
Mnemonic: AMERICA
- Age (greater than 65 years)
- Markers (raised serum cardiac markers)
- ECG (ST segment depression ≥0.5 mm at presentation)
- Risk factors (atleast 3 for coronary artery disease)
- Ischemia (atleast 2 anginal events previous 24 hours)
- Coronary stenosis (prior stenosis of 50% or more)
- Aspirin (use in previous 7 days)
1 point for each risk factor (maximum score 7).
Interpretation:
- Low risk: 0-2
- Intermediate risk: 3-4
- High risk: 5-7