Volume of aqueous: 0.25 ml (Anterior chamber) + 0.06 ml (Posterior chamber)
Composition of aqueous: similar to plasma except-
- higher concentration of ascorbate, pyruvate and lactate
- lower concentration of protein, urea and glucose
Functions of aqueous:
- Maintains Intra-ocular Pressure (IOP)
- Provides nutrition to avascular lens and cornea
- Optical transparency
- Place of lymph that is absent in eyeball
Production of aqueous:
- Source: ciliary process of ciliary body
- Rate: 2.3 µl/min
- Stages:
- Convective delivery: of H2O, ions, proteins, metabolic fuel by ciliary circulation.
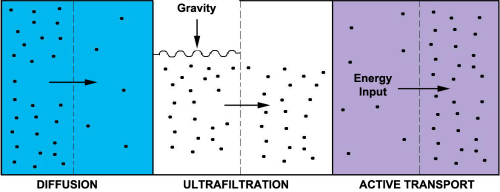
- Ultrafiltration and diffusion: from capillaries into the stroma, driven by oncotic pressure, hydrostatic pressure and concentration gradient.
- Active secretion: into the basolateral spaces between nonpigmented epithelium followed by water movement down the resultant osmotic gradient into posterior chamber.
Drainage of aqueous:
Ciliary process → Aqueous in posterior chamber → (though pupil) → Anterior chamber
From anterior chamber, the drainage pathway divides into 3 systems:
1. Trabecular/conventional/pressure dependent (90%):
Trabecular meshwork (innermost uveal, middle corneoscleral, outermost juxtacanalicular) → Schlemm’s canal (endothelial lined and present in scleral sulcus) → Collector channels (Direct – Aqueous vein; Indirect – Intrascleral plexus) → Episcleral veins
2. Uveoscleral/Unconventional/Extracanalicular/Pressure-independent (10%):
Ciliary body → Suprachoroidal space → Venous circulation of ciliary body, choroid and sclera
3. Iris outflow (<1%)
Intraocular Pressure (IOP):
Definition: Pressure exerted by intraocular fluids on the coats of the eyeball.
Normal value: 10-21 mmHg (16 +/- 2.5 mmHg)
Goldmann equation:
Pο = (F/C) + PV
where,
Pο = IOP = 10-21 mmHg
F = Rate of aqueous production = 2 µl/min
C = Facility of outflow = 0.22-0.28 µl/min/mmHg
PV = Episcleral venous pressure = 8-12 mmHg
Influencing factors:
1. Long term: Heredity, age, sex, race, refractive error
2. Short term:
- General:
- Posture: increased in supine position, highly increased in head down position
- Exercise: decreased by aerobic exercise, increased by isometric exercise
- Systemic:
- Valsalva: increased
- Food/drugs:
- lowers IOP: alcohol, fat-free diet, vasodilators, heroin, miotics
- increases IOP: water drinking, caffeine, steroids, mydriatics
- General anesthesia: lowers IOP except Ketamine and Succinylcholine
- Rhythmic:
- Cardiovascular: 1-2 mm
- Respiratory: upto 5 mm
- Diurnal (higher in morning): < 5 mm
IOP measurement:
Indications:
a. All suspected cases of glaucoma:
- Significant diurnal variation (>8 mm Hg)
- Significantly positive water drinking provocative test (>8 mmHg)
- > 0.2 asymmetry of cup to disc ratio in 2 eyes
- Splinter hemorrhage over or near disc
- Positive family history
- IOP constantly > 30 mmHg
- Diabetic and high myopic patient
b. Age: > 40 years
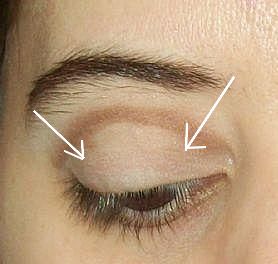
Techniques:
a. Digital palpation tonometry:
- The patient is asked to look downward
- Fluctuation of eyeball is elicited at upper lid with the help of index finger of 2 hands.
- Increased IOP: firm and hard
- Normal IOP: Soft (like a partially filled water bag)
b. Indentation (Schiotz) tonometry
c. Applanation (Goldmann’s) tonometry
How to master digital tonometry,
Due to sky rocketing prices of modern tonometry devices like Diaton tonopen etc it becomes practically impossible to afford.
Having been in rural eye examination outreach I’m often confronted with cases that need accurate Intraocular pressure IOP test.
War against irreversible visual impairment is winnable.
Dr. Benjamin Kish