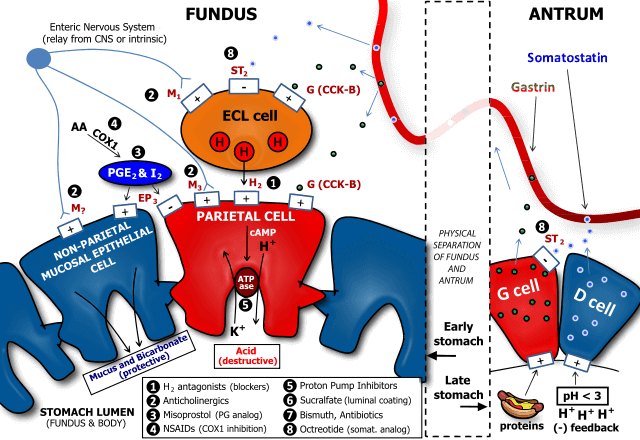
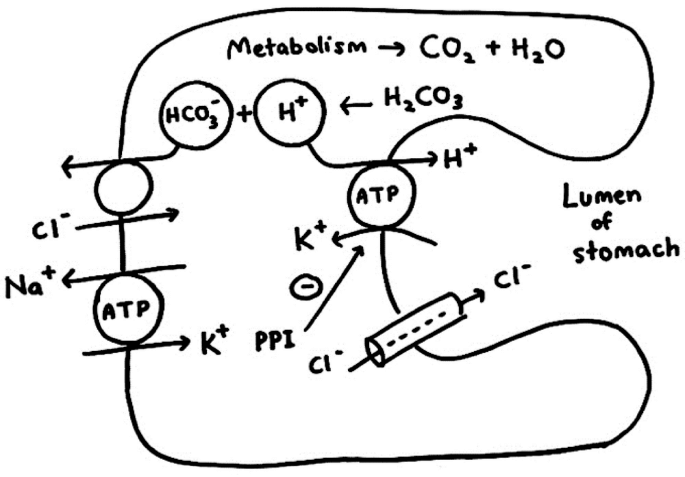
Steps for gastric acid secretion by parietal cells
1. H+ and HCO3- are produced from CO2 and H2O.
2. H+ is secreted into the lumen by H+/K+ ATPase pump.
3. HCO3- moves out of the cell, across the basolateral membrane via antiport with Cl-.
4. Cl- diffuses passively into the lumen via Cl- channel.
Phases of Gastric Acid Secretion
| Phases | Acid production | Trigger | Mechanism | Inhibition |
| 1. Cephalic | 30% | Psychic stimuli | Vagal stimulation | Loss of appetite/Depression (lack of parasympathetic center stimulation) |
| 2. Gastric | 60% | Presence of food in stomach (mechanical and chemical) | Distension: Vagovagal and local reflex Chemical (high pH): G cells release Gastrin | Low PH: Gastrin secretion decreases Emotional distress: Sympathetic stimulation |
| 3. Intestinal | 10% | Presence of food in duodenum (chemical) | Chemical (low pH): Intestinal gastrin released | Distension, Fatty acids, Hypertonic chyme: a. Enterogastric reflex b. Intestinal hormones (secretin, GIP, CCK, VIP) |
Pharmacology
1. Reduction of gastric acid secretion: H2 antihistaminics, Proton pump inhibitors (PPI), M1 anticholinergics, PG analogs (EP3 receptor)
2. Neutralization of gastric acid: Antacids
3. Ulcer protectives: Sucralfate, Bismuth, PG analogs
4. Ulcer healing: Carbenoxolone
5. Anti-H. pylori medications: Amoxicillin, metronidazole, tinidazole, tetracycline
Gastrointestinal peptides
| Name | Source | Stimulus | Mechanism | Action |
| Gastrin | G cells (gastric antrum) | Stomach distension | Hormone | HCl, pepsinogen, IF secretion Gastric motility Trophic to gastric mucosa |
| CCK | I cells (duodenum) | Partially digested peptides and triglycerides | Hormone | Enzyme rich pancreatic fluid Gallbladder contraction and sphincter of Oddi relaxation Gastric emptying reduction Trophic to pancreatic acinar cells Satiety |
| Secretin | S cells (duodenum/proximal jejunum) | Acid chyme, fatty acids | Hormone | Bicarbonate rich pancreatic fluid Gastric acid reduction Trophic to pancreatic acinar cells |
| VIP | Neuron (GI tract, pancreas) | Neural | Neurocrine | Pancreatic and intestinal secretion Inhibits gastric acid and pepsinogen secretion |
| Somatostatin | D cells (pancreas, stomach) | Fat, bile salts, glucose in intestinal lumen | Paracrine/Neurocrine | Decreases acid, pepsin, gastrin, pancreatic enzyme secretion Decreases insulin and glucagon Stimulates gastric mucous production |