Shapes of the female pelvis
Mnemonic: GAP (In order of most common to the least common)
- Gynecoid (50%) – normal female pelvis
- Anthropoid (25%) – direct occipito-posterior position is most common in anthropoid pelvis
- Android (20%) – male type (face to pubes delivery, persistent occipito-posterior position, deep transverse arrest/non-rotation, dystocia-dystrophica syndrome are most common in android pelvis)
- Platypelloid (5%)
Only pelvis with AP diameter > Transverse diameter is Anthropoid pelvis.
Mnemonic: ANthrOPoid
Android and Anthropoid (AN) pelvis are common causes of occipito-posterior (OP) presentation.
In platypelloid pelvis (broad and flat):
- Transverse diameter is much more than AP diameter
- Engagement by exaggerated posterior asynclitism occurs
- Super subparietal instead of biparietal diameter engages
Sub-public angle: It is formed by meeting of 2 descending pubic rami. It is 85 degrees in gynecoid pelvis.
Disorders:
- One ala of sacrum absent: Naegele’s pelvis (oNe = Naegele)
- Both ala of sacrum absent: Robert’s pelvis (Both = roBert)
Male Pelvis vs Female Pelvis
Mnemonic: Following structures are bigger in female – BIGS
- Body of pubis
- Ischial tuberosity
- Greater sciatic foramen
- Sub-pubic angle
Promontory and obturator foramen are larger in males.
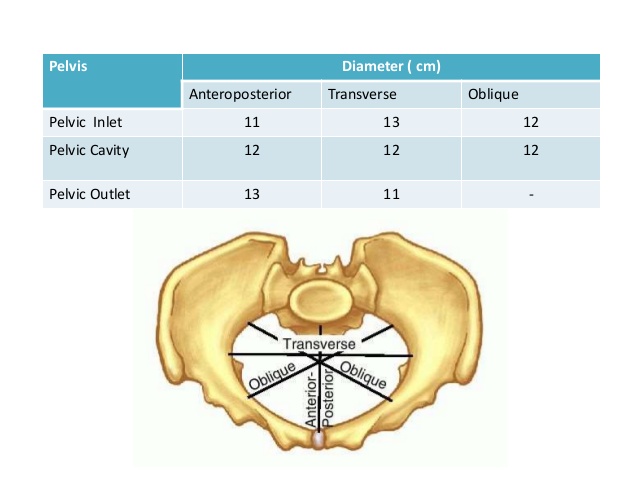
Pelvic Dimensions
It is not necessary to remember actual dimensions in centimeters or inches as written in the books. The dimensions can be measured at inlet, pelvic cavity and outlet.
Mnemonic: 11-12-13
| AP (11-12-13) | Transverse (13-12-11) | |
| Inlet | 11 cm | 13 cm |
| Cavity | 12 cm | 12 cm |
| Outlet | 13 cm | 11 cm |
A. Inlet:
- Antero-posterior diameters: Measured between sacral promontory and symphysis pubis
- Upper border of pubic symphysis: True or Anatomical conjugate
- Middle of pubic symphysis: Obstetric conjugate (most important)
- Lower border of pubic symphysis: Diagonal conjugate
- Transverse diameter: Measured between farthest 2 points on iliopectinate line
- Oblique diameter: Measured between the sacro-iliac (SI) joint and opposite ilio-pubic eminence
Mnemonic: DOT (from down to up)
- Diagonal conjugate (12 cm – largest)
- Obstetric conjugate (10 cm – smallest)
- True conjugate (11 cm)
B. Outlet:
- Antero-posterior diameters: From the lower border of symphysis pubis to –
- Anatomical: tip of coccyx
- Obstetric: tip of sacrum
- Transverse diameters:
- Bituberous diameter: between 2 ischial tuberosities
- Bispinous/Interspinous diameter: between 2 ischial spines (smallest pelvic diameter)
C. Pelvic cavity: Almost round
Dimensions in number:
AP diameter: Inlet (Anatomical conjugate) – 11 cm, Pelvic cavity – 12 cm and Outlet (Anatomical outlet) – 13 cm
Transverse diameter: Inlet – 13 cm, Pelvic cavity – 12 cm and Outlet (Intertuberous diameter) – 11 cm
Obstetric conjugate is the smallest AP diameter (10 cm). If <10 cm, it is called contracted pelvic inlet.
- Obstetric conjugate cannot be measured clinically but can be estimated by: Diagonal conjugate – 2.5 cm
Bispinous diameter is the smallest transverse diameter (10.5 cm).
Planes of pelvis
1. Plane of pelvic inlet: Makes an angle of inclination of 55 degrees with horizontal
2. Plane of least pelvic dimension (obstetric outlet): Lower border pubic symphysis – Ischial spines – Tip of sacrum
- Importance:
- Internal rotation occurs when occiput is in this plane.
- Marks the beginning of the forward curve of the pelvis.
- Most cases of deep transverse arrest occur here.
- Ischial spines represent zero station of head.
- External os lies at this level.
- Corresponds to origin of levator ani muscle.
- Landmark used for pudendal block.
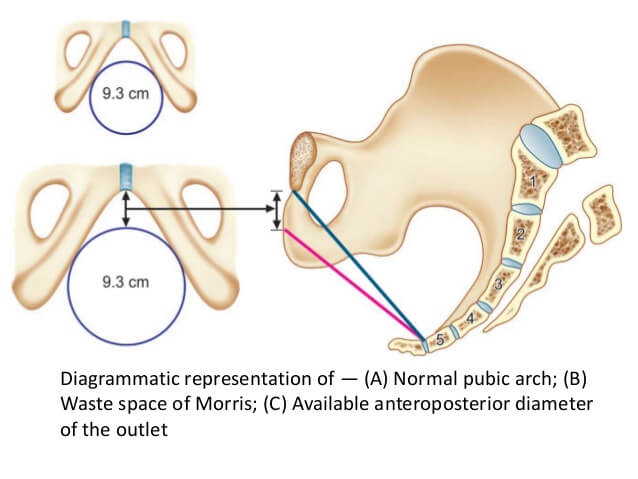
Waste Space of Morris
Normally, the width of the pubic arch is such that a round disk of 9.4 cm (diameter of a well-flexed head) can pass through the pubic arch at a distance of 1 cm from the midpoint of the inferior border of the symphysis pubis. This distance is known as the waste space of Morris.
In case of an inadequate pelvis with narrow pubic arch, the fetal head would be pushed backward and the waste space of morris would increase. As a result, reduced space would be available for fetal head to pass through, due to which the fetal head would be forced to pass through a smaller diameter called “available antero-posterior diameter). This is likely to injure the perineum or sometimes cause the arrest of fetal head.