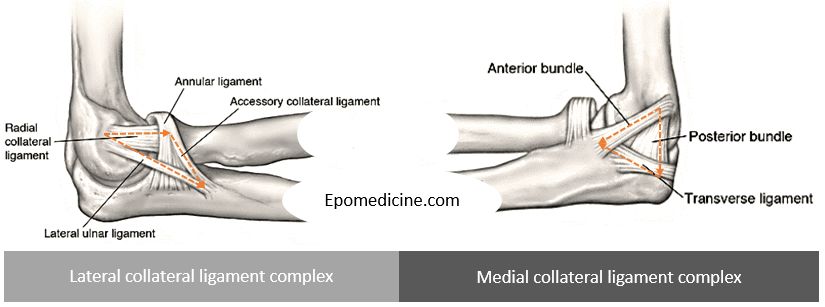
Lateral collateral ligament complex
Restraint to varus and posterolateral rotatory instability.
Anatomy is more variable.
LCL arises from lateral humeral condyle at a point through which the axis of rotation passes – it maintains a uniform tension throughout the arc of motion.
Annular ligament is a “U” shaped ligament that attaches to anterior and posterior portion of sigmoid notch (radial notch) of proximal ulna and encircles the radial head.
- Anterior insertion: taut in supination
- Posterior insertion: taut in pronation
The 3 other ligaments form a triangle with 3 points (lateral epicondyle, supinator crest of proximal-lateral ulna, annular ligament):
- Radial collateral ligament (RCL): Lateral epicondyle to Annular ligament
- Dimension: 20 X 8 mm
- Lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL): Lateral epicondyle to Supinator crest
- Accesory lateral collateral ligament: Annular ligament to Supinator crest
- Present in 33% population
- Stabilizes annular ligament
Key varus stabilizer: Lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL)
Medial collateral ligament complex
Restraint to valgus and posteromedial rotatory instability.
Anterior bundle attaches inferior to axis of rotation (always taut) and Posterior bundle attaches posterior and inferior to axis of rotation (taut in flexion >90 degrees).
The 3 ligaments form a triangle with 3 points (medial epicondyle, medial coronoid process and medial olecranon):
- Anterior bundle (anterior oblique): Medial epicondyle to medial coronoid process (sublime tubercle)
- 4 ot 5 mm width
- Posterior bundle (bardinet ligament): Medial epicondyle to olecranon (sigmoid notch)
- 5 to 6 mm width
- Transverse bundle (ligament of cooper): Medial olecranon to medial coronoid process
Key valgus stabilizer: Anterior bundle of MCL
Other ligaments
- Quadrate ligament: Anterolateral ulna to Anterior radial neck (under annular ligament).
- Tight in supination, stabilizes joint during prono-supination
- Oblique cord: Proximal lateral ulna Radial neck
- Prevents downward movement of radius, stabilizes joint during prono-supination
Capsule
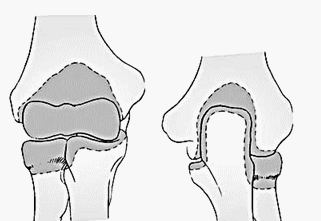
Anterior capsule:
- Proximally: above coronoid and radial fossa
- Distally: coronoid medially and annular ligament laterally
Posterior capsule:
- Proximally: just above olecranon fossa
- Distally: medial and lateral articular margin of sigmoid notch
Greatest capacity of elbow occurs at 80 degrees flexion and is 25-30 ml. Capsule is a secondary stabilizer.