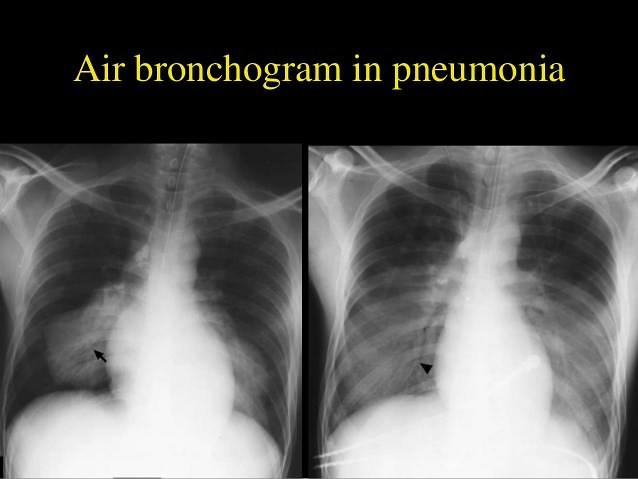
Clinical features
A. Adolescents and Adults
Mnemonic: 6 Ps (by Hargens and Mubarak)
- Pain (may be absent in cases of nerve damage):
- Pain out of proportion to other physical findings (requiring increasing analgesic requirement) *: Earliest symptom
- Pain on passive stretch of the muscles in concerned compartment *
- Low sensitivity and high specificity (large false-negative or missed cases)
- Pressure*: Tense and rigid swelling
- Higher sensitivity and lower specificity compared to other signs
- Paresthesia and hypesthesia (late sign): In the territory of the nerves traversing the affected compartment
- Low sensitivity and high specificity
- Paralysis (late sign):
- Worst clinical sign or symptom
- Poor prognostic indicator
- Pallor (late sign)
- Pulselessness (late and omnious sign)
*most important clinical signs and symptoms
| 4 Ps | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Positive predictive value (%) | Negative predictive value (%) |
| Pain | 19 | 97 | 14 | 98 |
| Paralysis | 13 | 97 | 11 | 98 |
| Paresthesia | 13 | 98 | 15 | 98 |
| Pressure (swelling) | 54 | 76 | 70 | 63 |
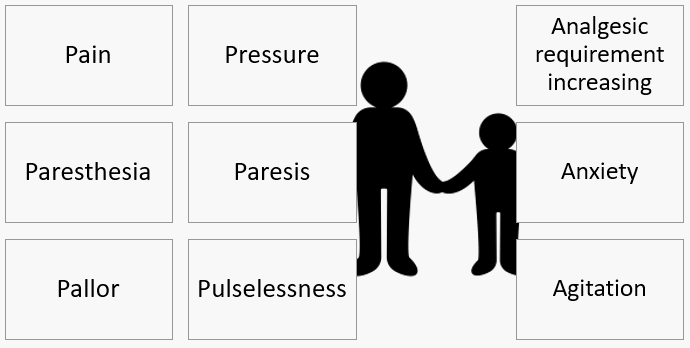
B. Young Children
Mnemonic: 3 As (by Noonan and Mcarthy)
- Anxiety
- Agitation
- Analgesia requirement increasing
- Earlier and more sensitive indicator of Pediatric ACS than neurovascular changes or uncontrolled pain
- May precede neurovascular changes by upto 7 hours
Note: Clinical features of compartment syndrome are more suggestive in their absence in ruling out the diagnosis than in confirming the diagnosis by their presence.