ACS recommendations (2015)
For women with average risk:
- 40-44 years: mammogram on patient’s choice
- 45-54 years: mammogram yearly
- >54 years: mammogram 2 yearly or yearly based on patient’s choice
- Women must be informed on the benefits and harms of mammographic screening
- Regular clinical breast exam and breast self-exam are not recommended due to lack of evidence 1
For women with higher risk: MRI in addition to mammography each year 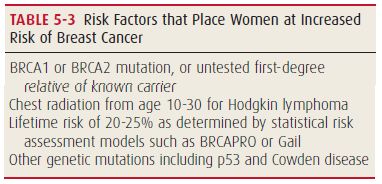
Learn about risk factors for Breast Cancer.
Mammography
Low voltage, high amperage Xray (300 mA, 40 KV)
Radiation dose: 0.1 cGy (Chest Xray only delivers 25% of this dose)
Sensitivity: 85-90%
Procedure:
- Selenium coated X-ray plate is used directly in contact with breast
- 2 views: Mediolateraloblique (MLO – 45 degrees angle along the border of pectoralis major) and Cranio-caudal (CC)
- Film labels are by convention located on the lateral aspect of a CC view and the superior aspect of an MLO view, allowing the reader to determine the quadrant wherein an abnormality is located
Indications:
- Screening mammography: As per ACS recommendations
- Diagnostic mammography: Assess clinical findings (palpable abnormality, persistent focal pain/tenderness, bloody/clear nipple discharge, skin changes), Finding detected on screening mammogram requiring further evaluation, Short interval followup for Bi-RAD 3, Asymptomatic patients previously treated for breast cancer, Rule out multifocal involvement in same breast to plan BCT (Breast Conserving Therapy), Rule out involvement of contralateral breast
Findings:
- Differences in density of breast tissue
- Architectural distortion of tissue planes
- Asymmetry such as nipple retraction
- Calcifications ranging from benign involutional changes to suspicious microcalcifications that can be described as pleomorphic, clustered, linear, or branching
Relative contraindications: Women with symptoms or signs of breast cancer (screening may delay management), Age <40 years with average risk, Pregnancy, Women with breast implants (less sensitive)
Risk: Radiation exposure, Pain, False positives (10%), False negatives (6-8%), Overdiagnosis
Digital Mammography: By directly converting the detected x-ray photons to numerical values, the process of x ray photon detection is decoupled from the image display. The digital images can be processed by a computer, displayed in multiple formats, and fed directly to computer-aided detection (CAD) software programs.
Whole Breast Ultrasonography
Screening US appears to be more sensitive in detecting early invasive cancer whereas mammography is more sensitive in the detection of calcifications associated with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
Although US is less sensitive than MRI, due to its lower cost and availability, it is likely that whole-breast US will play an increasing role as a supplemental screening modality in women with dense breasts.
Contrast-Enhanced Breast MRI screening
Indications: useful tool as an adjuvant to screening mammography in women at high risk for breast cancer
Sometimes women don’t even get an idea about their breast health until the higher stages of breast cancer. This is a great content in order to learn about breast cancer screening in a very easy to understand context.