Bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction (BIND) Score is used to assess bilirubin induced encephalopathy in neonates with severe hyperbilirubinemia. Johnson et al developed the BIND score to help identify an infant who requires more aggressive monitoring and management.
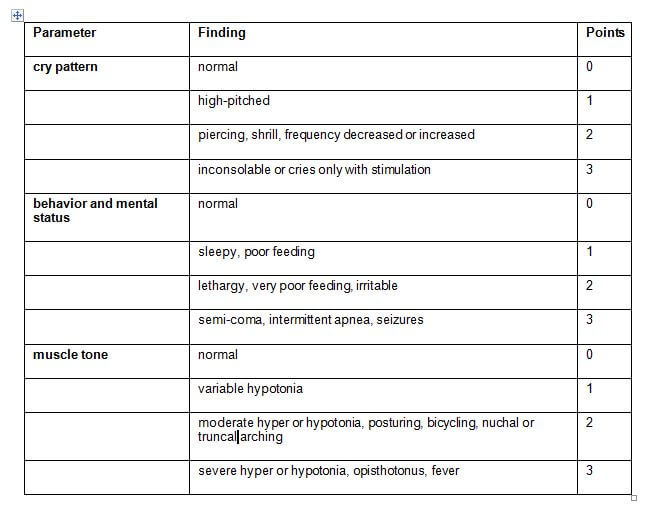
The scoring system has 3 parameters:
1. Cry pattern
2. Behavior and mental status
3. Muscle tone
BIND score = Total score (Points for all 3 parameters scored separately and added)
Interpretation:
- minimum score: 0
- maximum score: 9
| BIND Score | Stage |
| 1 to 3 | Stage 1A |
| 4 to 6 | Stage 1B |
| 7 to 9 | Stage II |
Stages of BIND:
| Stage of BIND | Features |
| IA | minimal signs; totally reversible with therapy |
| IB | progressive signs but reversible with therapy |
| II | irreversible signs but severity decreased with prompt and aggressive therapy |
References:
Johnson L, Brown AK, Bhutani VK. BIND – A clinical score for bilirubin induced neurologic dysfunction in newborns. Pediatrics. 1999; 104 (Supplement): 746-747.
Resource for reading: http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/134/5/e1330

MD Pediatrics and Fellowship Neonatology, he chooses to stay anonymous. He often writes his views online as well as share few important topics for medical students, doctors and specially parents. He does research in pediatrics.