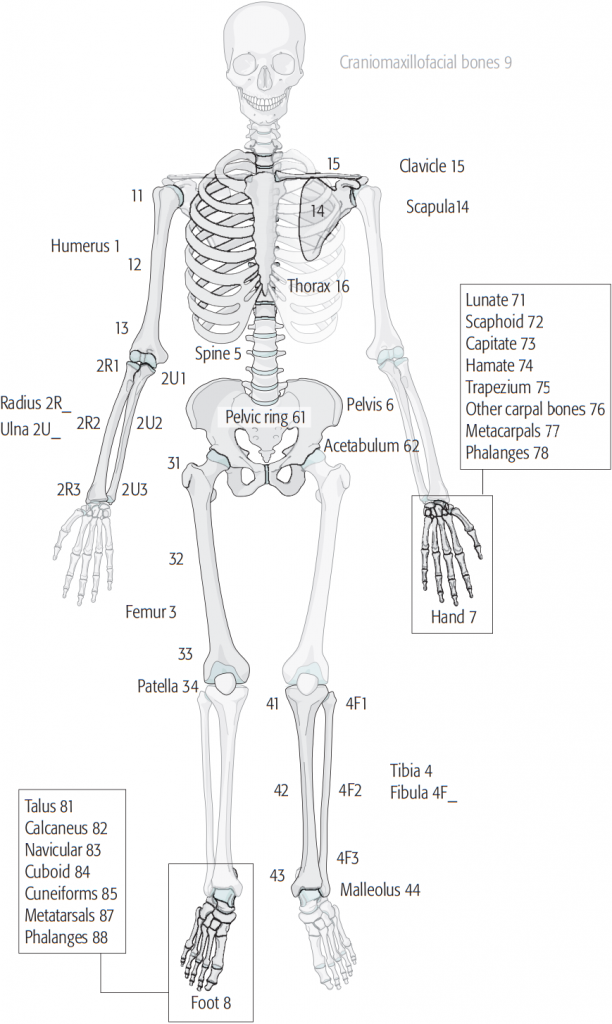
It is an alpha-numeric system of classification developed by Muller and colleagues.
Step 1: 1st digit specifies bone
- 1 = Humerus and Shoulder bones
- 2r/u = Radius/Ulna
- 3 = Femur
- 4t/f = Tibia/Fibula
- 5 = Spine
- 6 = Pelvis/Acetabulum
- 7 = Hand
- 8 = Foot
- 9 = Craniomaxillofacial bones
Step 2: 2nd digit specifies segment of bone
- 1 = Proximal end/Pelvic ring
- 2 = Diaphyseal/Acetabulum
- 3 = Distal end
- 4 = Scapula/Patella/Malleolus (14, 34, 44 respectively)
- 5 = Clavicle (15)
Square definition: Proximal and distal segments are defined by a square whose sides = length of widest part of epiphysis
Exceptions of square definition:
- Proximal femur = above a line that passes transversely through the inferior edge of the lesser trochanter
Doesn’t separate metaphysis and epiphysis in proximal and distal segments
Step 3: Alphabet and numbers represents fracture pattern
1. Diaphysis:
- A = Simple
- 1 = Spiral
- 2 = Oblique (>30 degrees)
- 3 = Transverse (<30 degrees)
- B = Wedge
- 1 = Spiral wedge
- 2 = Bending wedge
- 3 = Fragmented wedge
- C = Complex
- 1 = Complex, spiral
- 2 = Complex, segmental
- 3 = Complex, irregular
2. Proximal and Distal ends:
- A = Extra-articular
- 1 = Metaphyseal simple
- 2 = Metaphyseal wedge
- 3 = Metaphyseal complex
- B = Partial articular
- 1 = Lateral condyle, sagittal
- 2 = Medial condyle, sagittal
- 3 = Frontal plane
- C = Complete articular
- 1 = Articular and metaphyseal simple
- 2 = Articular simple, metaphyseal multifragmentary
- 3 = Articular and metaphyseal multifragmentary
Exceptions:
a. Proximal humerus (11):
- A = Extra-articular unifocal
- B = Extra-articular bifocal
- C = Intra-articular
b. Proximal femur (31):
- A = Trochanteric
- B = Neck
- C = Head
c. Malleolar (44):
- A = Infra-syndesmotic
- B = Trans-syndesmotic
- C = Supra-syndesmotic
d. Spine:
- A = Compression fracture
- B = Distraction fracture
- C = Translation fracture
Source and further reading: https://classification.aoeducation.org/files/download/AOOTA_Classification_2018_Compendium.pdf