To obtain the correct weight for each age, assign each finger a chronological odd number starting with 1, representing the age in years. Now, using the same fingers, count in the multiples of 5, starting with 10 to obtain the corresponding ideal body weight in kilograms. For the even ages, add 2 to the prior odd weight or subtract 3 from the subsequent odd weight.
| Age (years) | Estimated weight (kg) |
| 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 12 |
| 3 | 15 |
| 4 | 27 |
| 5 | 20 |
| 6 | 22 |
| 7 | 25 |
| 8 | 27 |
| 9 | 30 |
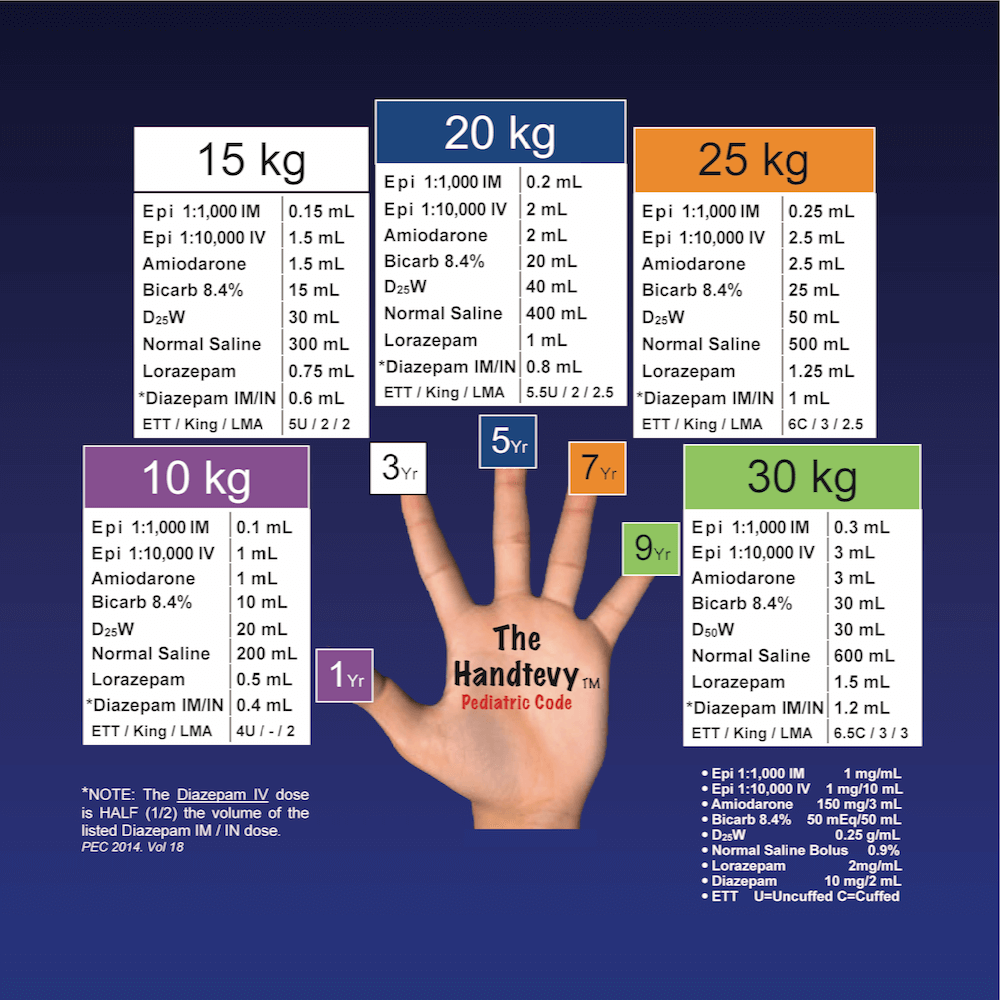
Handtevy Drug Volume in ml (Doses) by Weight
Epinephrine 1:1000 IM (1 mg/ml): Move the decimal point twice to left
Epinephrine 1:10000 IV (1 mg/10ml): Move the decimal point once to left
Amiodarone (150 mg/3ml): Move the decimal point once to left
Bicarbonate 8.4%: Same as weight
D25W: Double the weight
Normal saline bolus: Double the weight and move the decimal point once to right
Lorazepam (2 mg/ml): Half the weight and move the decimal point once to left
Example: For a 1 year child, estimated weight is 10 kg. The drug doses according to Handtevy method would be –
Epinephrine 1:1000 IM (1 mg/ml): 0.1 ml
Epinephrine 1:10000 IV (1 mg/10ml): 1 ml
Amiodarone (150 mg/3ml): 1 ml
Bicarbonate 8.4%: 10 ml
D25W: 20 ml
Normal saline bolus: 200 ml
Lorazepam (2 mg/ml): 0.5 ml
Pediatric weight estimation using the finger counting method for children between the ages of 1 and 9 is an acceptable alternative to the Broselow method. Predicted weights from the Handtevy age-based weight estimation method accurately predict pediatric normal weights.
Bella Vista, AR website reveals that this system has been federally approved as an alternative to PALS (Pediatric Advanced Life Support), in which members of Bella Vista’s EMS department are currently certified.
Further reading:
- Young TP, Chen BG, Kim TY, Thorp AW, Brown L. Finger counting: an alternative method for estimating pediatric weights. Am J Emerg Med. 2014 Mar;32(3):243-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Nov 26. PMID: 24370066.
- https://www.jems.com/patient-care/handtevy-method-helps-providers-rapidly/
Note: Data and information are provided for informational purposes only.