Risk factors
Mnemonic: ABCDE
- Aortic aneurysm
- Boys (male), Blood pressure (hypertension) and Bicuspid aortic valve
- Connective tissue disorders (Marfans, Ehlers-Danlos)
- Delivery and pregnancy
- Elderly (50-70 years) and Exercise (heavy weight lifting)
Pathophysiology
Intimal tear allows blood to enter between intima-media space creating a false lumen. Blood may propagate proximal or distal to tear.
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic
- Tearing chest pain radiating to back (interscapular)
- Pulse deficit and differential pressure in limbs
- Signs of end organ ischemia
Investigations
- ECG: rule out cardiac ischemia
- CXR: Widened mediastinum (>8 cm), tracheal shift
- CT angiogram (stable patients): gold standard (intimal dissection flap, double lumen, aortic dilation, contrast leak)
- Transesophageal echocardiography/TEE (unstable patients)
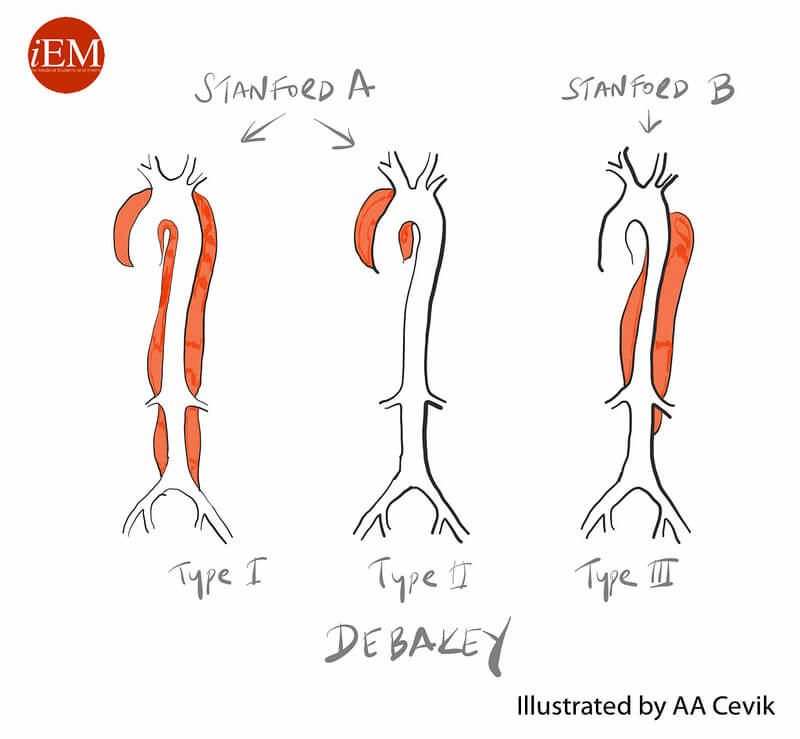
Classification and Management
| Stanford | DeBakey | Description | Frequency | Management |
| Mnemonic: BAD | Mnemonic: A for A; B for B | |||
| A (Ascending aorta involved) | I | Both (Ascending aorta and Descending aorta) | 60% | Arch replacement +/- Aortic root repair |
| II | Ascending aorta | 10-15% | ||
| B (Ascending aorta not involved) | III | Descending aorta | 25-30% | a. Uncomplicated – Beta blocker IV with aim: HR: 60-80 bpm SBP: 100-120 mmHg |
| a | above diaphragm | b. Complicated (rupture, ischemia, false lumen expansion, continuing pain) – Endovascular treatment (TEVAR) | ||
| b | below diaphragm |
a. <28/40 weeks – Aortic repair with fetus in utero
b. >32/40 weeks – Primary CS followed by aortic repair in same setting