ANGULAR STOMATITIS/CHEILITIS
Definition: Maculopapular and vesicular lesions grouped on the skin at the corners (or ‘angles’) of the mouth and the mucocutaneous junction. It is made worse by licking the lips.
Causes:
1. Oral candidiasis
2. Poorly fitting dentures
3. Bacterial infection
4. Less common
- Nutritional deficiencies (especially riboflavin, iron and pyridoxine)
- Iron and other nutrients are necessary in gene transcription for essential cell replication, repair and protection. Nutrient deficiency leads to impeded protection, repair and replacement of the epithelial cells on the edges of the mouth.
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Contact allergy
- Seborrheic or Atopic dermatitis
- Oral retinoid medications
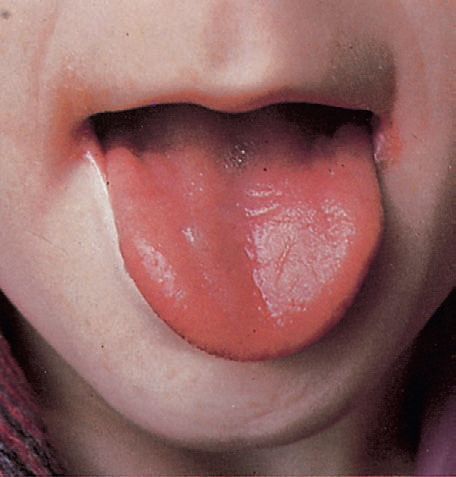
ATROPHIC GLOSSITIS
Definition: The absence or flattening of the filiform papillae of the tongue – the tongue appears smooth and erythematous “beefy”. In later stages, there may be shallow ulceration.
Causes:
- Associated with micronutrient deficiency, including:
- Iron deficiency
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Folic acid deficiency
- Thiamine deficiency
- Niacin deficiency
- Vitamin E deficiency
- Amyloidosis
- Sjögren’s syndrome
As cells of the tongue papillae have a high rate of turnover, deficiencies in micronutrients needed for cell proliferation or cell membrane stabilisation may lead to depapillation. Nutritional deficiency is also thought to change the pattern of microbial flora, thus contributing to glossitis.