1st Published in Pedchrome in January 1, 2015
Case Summary
A 6-year-old patient was found to have course facial features and short stature. Parents have noticed a developmental stasis since 4-5 years of age. The weight was normal. There were no any chronic illness, any significant birth and postnatal history contributing to the condition. There was no history of short stature or pubertal delay in the family members. Nutritional status was good.
On examination: The child had coarse facial features, with low anterior hair line and prominent angles of face. Looked stunted and no skin changes, no thyroid enlargement. Abdominal examination revealed Hepatosplenomegaly. Cornea was clear but sclera looked muddy.
There was no major limb deformity or bending. No pallor.
Anthropometric measurements:
- Height: less than 3rd centile
- Weight/Height: Normal
- Upper segment to Lower segment ration: 1:1 at 6 years
- Arm span: Normal
We suspected Mucopolysaccharidosis.
Differential diagnoses:
- Hypothyroidism
- Mucolipidosis
- Other metabolic storage disorders
As TSH and T4 were normal, hypothyroidism was ruled out. Other conditions were less likely from clinical information and findings.
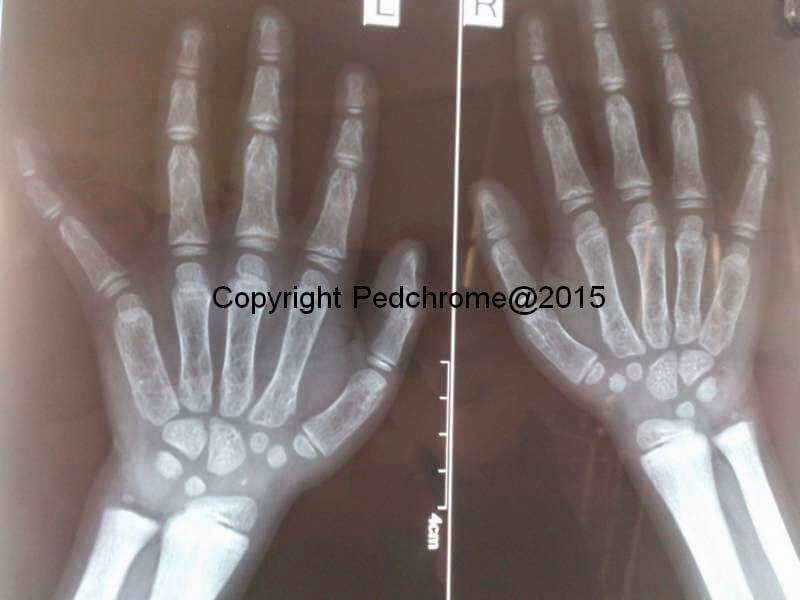
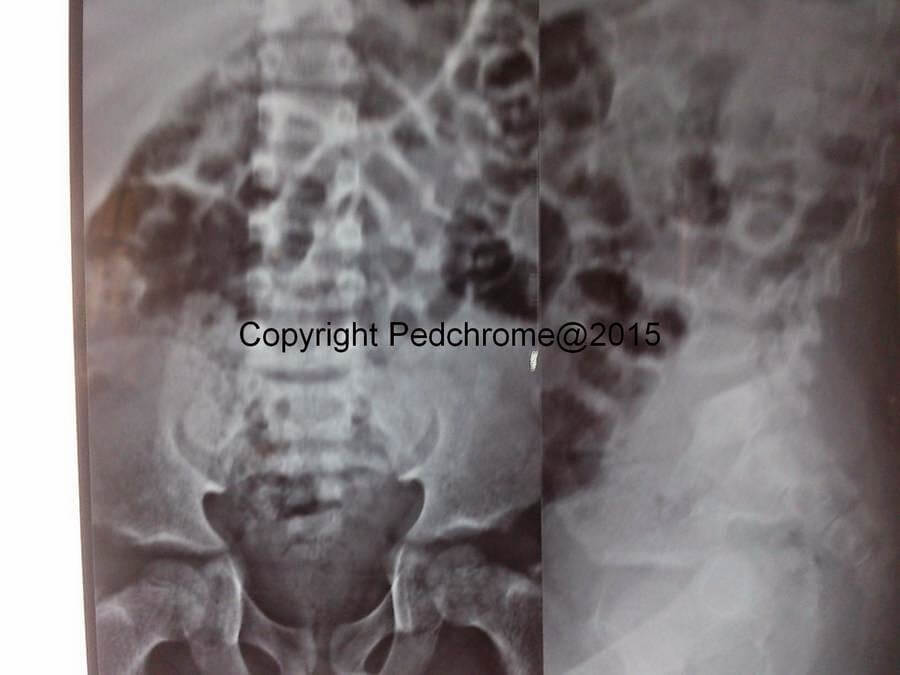
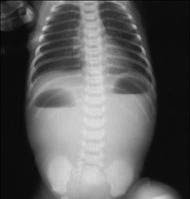
Xray of Hand and Spine:
- Hand: Increased trabeculation with bullet shaped phalanges. Bone trabeculation is coarse and the cortices are thin.
- Spine: mild changes with beaking of vertebrae.
Review of Mucopolysaccharidosis
Mucopolysaccharidoses are hereditary, progressive diseases caused by mutations of genes coding for lysosomal enzymes needed to degrade glycosaminoglycans. Products of GAG, Keratan sulphate, Dermatan Sulphate , chondroitin sulphate accumulates in body and cause various manifestations.
As a general rule, the impaired degradation of heparan sulfate is more closely associated with mental deficiency and the impaired degradation of dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfates, and keratan sulfate with mesenchymal abnormalities
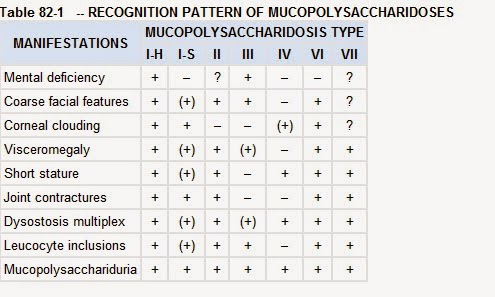
There are 7 variants. Recognition of type depends on clinical manifestations, severity and corneal involvement.
I- Hurler Syndrome
II- Hunter Syndrome
III- San Filippo
IV- Morquio
VI-Maroteaux-Lamy
VII- Sly
IX- Hyaluronidase deficiency
Among these all are inherited via Autosomal recessive inheritance except Hunter Syndrome which is an X-linked disorder.
Here is a summary of involvement of organs in different MPS variants:
Hepatosplenomegaly, coarse facial features, short stature (disproportionate) with bony changes and mental deficiency are the main features. Corneal clouding in seen in most variants as disease progresses except in Hunter and San Filippo syndromes.
In this Child:
We found short stature, coarse facial features, Dysostosis multiplex, Clear Cornea and visceromegaly with minimal mental deficiency – likely to be Hunter Syndrome.
Investigations:
Routine CBC, LFT, RFT and urine were normal in the child. On evaluation eye was normal, no cherry red spots on retina.
Urinary GAG quantification was too expensive and could not be done in this patient. Likewise genetic analysis and carrier mapping was not feasible.
Treatment Options:
Available options today are-
1. Hematopoietic Stem cell transplant: which can be curative. If done before 2 yrs can prevent progression of mental deficiency but this modality does not treat bone and eye problems.
Transplantation prevents neurocognitive degeneration but does not correct existent cerebral damage. Hence, the main target group are young children with severe MPS I, anticipated neurodegeneration, who undergo transplantation before 24 months of age and have a baseline mental development index >70.
2. Replacement Therapy: recombinant enzymes is approved for patients with MPS I, MPS II, and MPS VI.
3. Management of Complications: like Hydrocephalus, Orthopedic and vision issues etc.
As we could not objectively prove our Diagnosis, if you have a different diagnosis or opinion for this case, you are free to comment.

MD Pediatrics and Fellowship Neonatology, he chooses to stay anonymous. He often writes his views online as well as share few important topics for medical students, doctors and specially parents. He does research in pediatrics.