Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy is a term that encompass wide range of blood pressure related disorders during pregnancy like gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, etc.
Blood pressure in Normal Pregnancy:
During middle trimester, due to the reduction in Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR) and Arterio-venous (AV) shunting within the uterus and intervillous space – the Blood Pressure (BP) falls below pre-pregnancy or early pregnancy level. This is compensated by relative tachycardia. In the 3rd trimester, BP usually rises back to the pre-pregnancy level.
Criteria for diagnosis of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy:
- If previous Blood pressure (BP) is not known: Absolute BP ≥140/90 mm Hg, taken on two separate occasions 6 hours apart
- If pre-pregnant or first trimester BP is known: Systolic BP + ≥30 mmHg and Diastolic BP + ≥15 mmHg
Classification of Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy:
1. Chronic hypertension: Hypertension diagnosed before pregnancy or before 20 weeks of pregnancy. It can be either essential or secondary.
2. Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH): New onset hypertension diagnosed after 20 weeks of pregnancy. It includes:
- Gestational Hypertension
- Pre-eclampsia
- Eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia and Eclampsia are often referred to as Toxemia of pregnancy.
| Classification | Gestational weeks | Blood pressure (mmHg) | Proteinuria | Seizures | Additional features |
| Gestational hypertension | > 20 | > 140/90 | No | No | |
| Mild pre-eclampsia | > 20 | 140-160/90-110 | >300mg/24 hrs or ≥1+ dipstick | No | |
| Severe pre-eclampsia | >20 | >160/110 | >5g/24 hrs ≥3+ dipstick | No | End-organ dysfunction |
| Eclampsia | >20 | >160/110 | >5g/24 hrs | Yes | End-organ dysfunction |
| Chronic hypertension | <20 or prior to pregnancy | >140/90 | No | No | |
| Superimposed pre-eclampsia | <20 | >140/90 | New onset >0.5 g/2 hrs | No | Thrombocytopenia or Raised Liver enzymes |
Incidence of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy:
- About 10% pregnant women develop hypertension and mild pre-eclampsia
- Further 10% of these develop severe pre-eclampsia
- Incidence of eclampsia ranges from 1 in 500 to 1 in 30
Risk Factors for hypertensive disorders in pregnancy:
- Primigravida
- Positive family history and past history
- Placental abnormalities:
- Hyperplacentosis: Molar pregnancy, Multiple pregnancy, Diabetes mellitus
- Placental ischemia
- Obesity
- New partner
- Chronic hypertension
- Thrombophilias: Antiphospholipid syndrome, Protein C or S deficiency, Factor V Leiden
Pathophysiology:
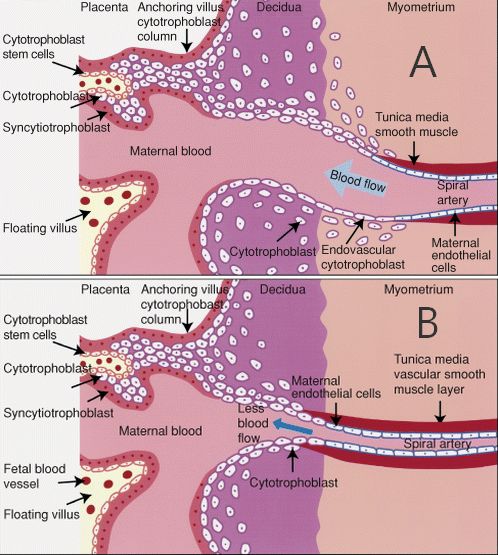
In normal pregnancy, cytotrophoblasts invade the uterine spiral arterioles, converting them from small-caliber vessels to large-caliber capacitance vessels capable of carrying larger amount of blood flow through the placenta. In pre-eclampsia events are postulated to occur in following steps:
- Defective cytotrophoblast invasion
- Deficient transformation of the spiral arterioles
- Reduced placental perfusion
- Increased secretion of antiangiogenic factor from hypoperfused placenta
- Antagonism of proangiogenic effects of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and placental growth factor
- Systemic vascular endothelial dysfunction
- Increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), thromboxane (TX-A2), and endothelin-1 (ET-1) and Increased vascular sensitivity to angiotensin II and decreased nitric oxide (NO) and prostacyclin (PGI2) bioavailability
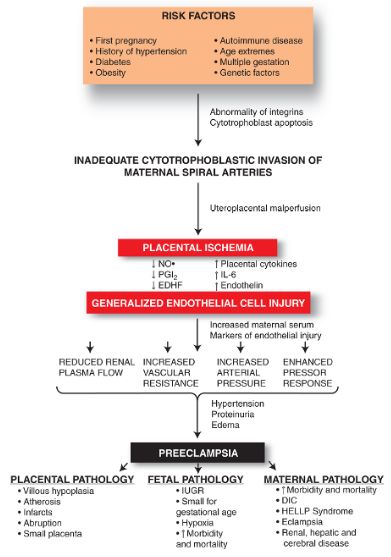
- Potent vasoconstriction and end-organ damage:
- Neurologic: Headache, Blurred vision, Visual scotomata, Hyperreflexia, Clonus, and seizures. Cerebral edema and intracerebral hemorrhage can be seen.
- Renal: Proteinuria (>300 mg/day), Azotemia (decreased renal blood flow and average GFR by 30-40%), Acute Kidney Injury (usually due to Acute Tubular Necrosis), Increased urate reabsorption (leads to hyperuricemia)
- Hematologic: Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, Thrombocytopenia, DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation)
- Hepatic: HELLP syndrome (Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, Low Platelets)
- Cardiovascular: Hypertension, decreased cardiac output
- Gastrointestinal: Elevated liver enzymes, epigastric/right upper quadrant pain, subcapsular hemorrhage, liver rupture
- Other: Pulmonary edema, Peripheral edema