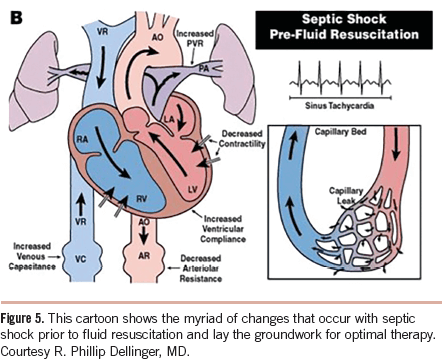
Endpoints of resuscitation
MAP: > or = 65 mmHg
Urine output: > 0.5 ml/kg/hr; despite ↓RBF (Renal Blood Flow) it can be normal due to –
- Atrial natriuretic factor are elevated in sepsis
- Hypoproteinemia in sepsis – low plasma colloid osmotic pressure is less able to facilitate oncotic reabsorption.
CVP: 8-12 mmHg; may be unreliable due to –
- decreased ventricular compliance, increased airway pressure from ventilation, tricuspid regurgitation, pulmonary hypertension, and ventilation/perfusion abnormalities in the lung
Oxygen delivery and oxygen consumption: SvO2 > or = 65%
- Oxygen delivery (mL/min) = CO (L/min) X Hb concn. (g/dL) X 1.34 (mL O2/g Hb) X % SaO2
- Oxygen consumption = CO X (SaO2-SvO2) X 1.34 (Hb concn.)
- An SvO2 less than 50% is highly suggestive of decreased perfusion
- SvO2 may be high in sepsis due to increased blood flow to metabolically inactive tissue
Lactate/base excess: Serial ABG measurements (>4 mmol/l ~ severe sepsis)
- Increased glycolysis (increased pyruvate) with inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase (by endotoxin)
Echocardiography and Doppler:
- Changes in aortic blood flow velocity with respiration (accurate if systolic function is preserved)
Pulse pressure variability with respiration:
- As patients become more hypovolemic, pulse pressure variability increases.
Sepsis Bundle as per Surviving Sepsis Campaign
TO BE COMPLETED WITHIN 3 HOURS OF TIME OF PRESENTATION:
1. Measure lactate level
2. Obtain blood cultures prior to administration of antibiotics
3. Administer broad spectrum antibiotics
4. Administer 30ml/kg crystalloid for hypotension or lactate ≥4mmol/L
TO BE COMPLETED WITHIN 6 HOURS OF TIME OF PRESENTATION:
5. Apply vasopressors (for hypotension that does not respond to initial fluid resuscitation) to maintain a mean arterial pressure (MAP) ≥65mmHg
6. In the event of persistent hypotension after initial fluid administration (MAP < 65 mm Hg) or if initial lactate was ≥4 mmol/L, re-assess volume status and tissue perfusion.
7. Re-measure lactate if initial lactate elevated. 1
Basic Approach to Early Goal Directed Therapy (EGDT)
- Crystalloids or colloids if CVP <8
- Vasoactive agents when CVP goals will be met but mean arterial pressure (MAP) remains <65 mm Hg
- ScVO2 of < 70% for transfusion of packed red blood cells to target hematocrit of 30% (or the use of inotropic agents if hematocrit already >30%)
Fluid Resuscitation Recommendations
- Crystalloid or colloid – Crystalloid as first choice; HES not to be used and albumin to be used when large volume of crystalloids is required
- Initial fluid challenge – atleast 30 mL/kg of crystalloids (or colloid equivalent)
- Fluid challenge continued – until hemodynamic improvement either based on:
- dynamic (eg, change in pulse pressure, stroke volume variation) or
- static (eg, arterial pressure, heart rate, CVP) variables. 2
Vasopressor Recommendations
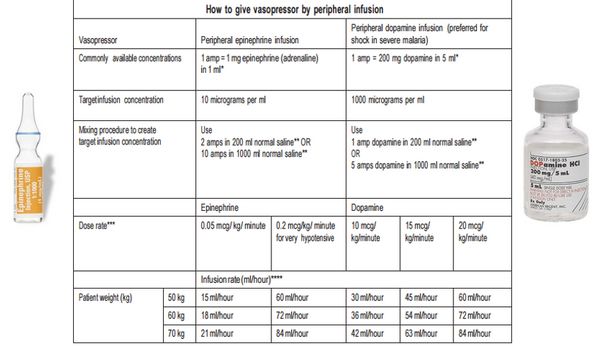
- Indicated if MAP <65 mmHg despite fluid challenge
- Vasopressors may be started from peripheral line but central line must be established as soon as possible.
- 1st choice: Norepinephrine (NE)
- Start with a dose rate of 0.1 microgram/kg/min and titrate upward as needed.
- Dose rates up to 3.3 microgram/kg/min are successful in raising the blood pressure in most cases.
- If the desired MAP is not achieved at a dose rate of 3–3.5 microgram/kg/min, add a second vasopressor.
- Norepinephrine is favored by many because it is more likely to raise the blood pressure than dopamine, and is less likely to promote arrhythmias. 3
- Epinephrine may be added to norepinephrine or replace norepinephrine to maintaing target goals if not achieved
- Vasopressin 0.03 units/minute can be added to NE to raise MAP or decrease NE dosage.
- Doses higher than 0.03-0.04 units/minute as a salvage therapy (reserved for failure to achieve adequate MAP with other vasopressor agents)
- Vasopressin is a pure vasoconstrictor that can promote splanchnic and digital ischemia, especially at high dose rates.
- Dopamine can be used instead of norepinephrine only if patient has low cardiac risk
- Start at a dose rate of 5 microgram/kg/min and titrate up-ward as needed.
- Vasoconstriction is the predominant effect at dose rates above 10 microgram/kg/min.
- If the desired MAP is not achieved with a dose rate of 20 ∝g/kg/min, add NE as a second vasopressor.
- Reno-protective low dopamine dosing is a myth.
- Phenylephrine can be used only when:
- Serious arrhythmias associated with norepinephrine
- High cardiac output with low blood pressure persistently (phenylephrine is a potent vasoconstrictor)
- As salvage therapy when combined vasopressors have failed to achieve MAP target
Blood Products Recommendations
- Once tissue hypoperfusion has resolved and in the absence of myocardial ischemia, RBC transfusion to be carried only when hemoglobin concentration decreases to <7.0 g/dL
- Target adult hemoglobin 7.0 –9.0 g/dL
- Erythropoietin should not be used as a specific treatment of sepsis associated anemia
- Fresh frozen plasma to be used only in cases of active bleeding or planned invasive procedure in the setting of deranged clotting profiles.
- Antithrombin not to be used for the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock