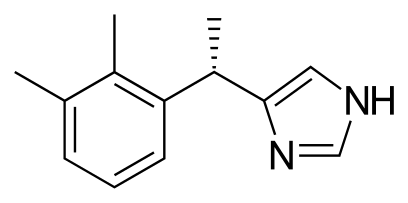
Mnemonic: BARASH Uses of Dexmedetomidine: This mnemonic, BARASH, is dedicated to Dr. Paul G. Barash, whose work in anesthesiology has profoundly shaped medical education and clinical practice. Just as his textbook has guided countless practitioners, may this mnemonic serve as a concise tool for remembering key concepts with clarity and…
Tag: Pharmacology
How to Get Over Long-Term Prescription Opioid Use Following Surgery
Most people walk into surgery expecting that the after-effects will fade with the stitches. Yet for many, the strongest echo of the operation is a small plastic bottle of prescription opioids that never seems to empty. When it comes to short-term pain, opioids can offer really effective relief. But when…

Thiocolchicoside vs Tizanidine vs Baclofen for Low Back Pain
Thiocolchicoside is widely used in acute muscular low back pain due to its fast-acting and less sedative profile. Tizanidine is better suited for chronic cases but requires monitoring due to sedative and hepatic effects. Baclofen is more useful for spasticity of CNS origin and is less commonly used for routine…
Antibiofilm Antibiotics
Biofilms are immobile microbial communities which colonize and grow on surfaces of medical implants such as sutures, catheters and implants, by self-produced extracellular polymeric substances and cause infections which can only be treated by their removal. It provides additional resistance to the bacteria by various mechanisms like altered pH, osmolarity,…
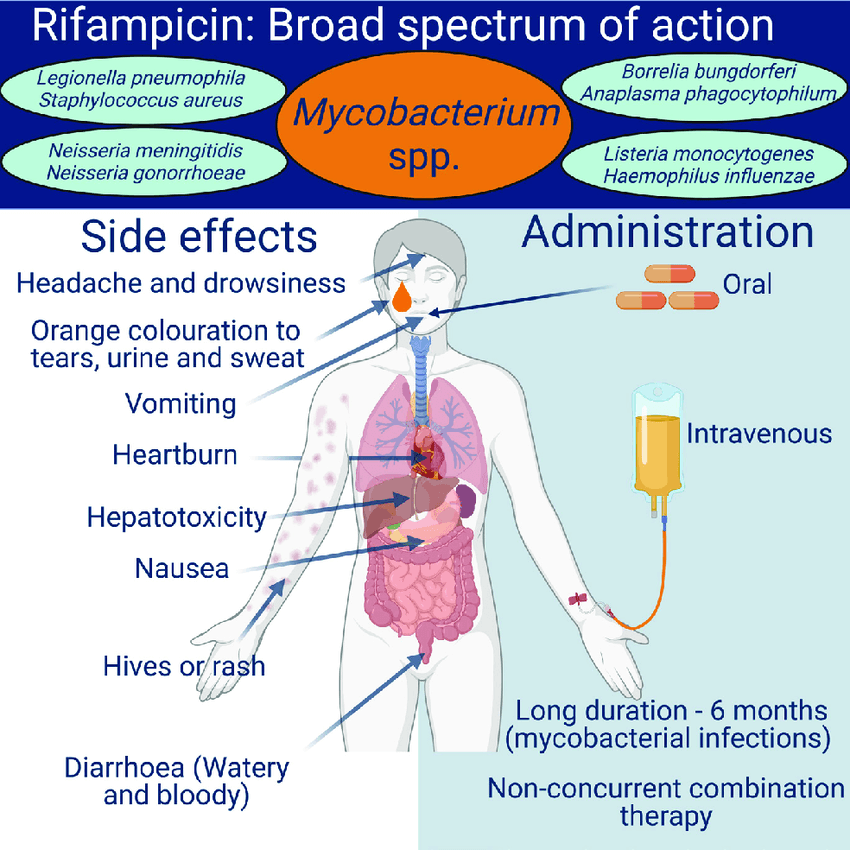
Rifampicin : Mnemonic
Synonym: Rifampin Mnemonic: RIFAMPIN R: RNA polymerase inhibition I: Induces CYP450 F: Flu-like symptoms, Fluid (sweat, urine, tears, saliva) discoloration A: AST/ALT elevation (Hepatotoxicity is a possible complication) M: Mycobacteria (M. Tuberculosis, M. Leprae, MAI treatment) and Meningitis (N. Meningitidis prophylaxis for close contacts) P: Penetrates granuloma, biofilm and blood-brain-barrier,…
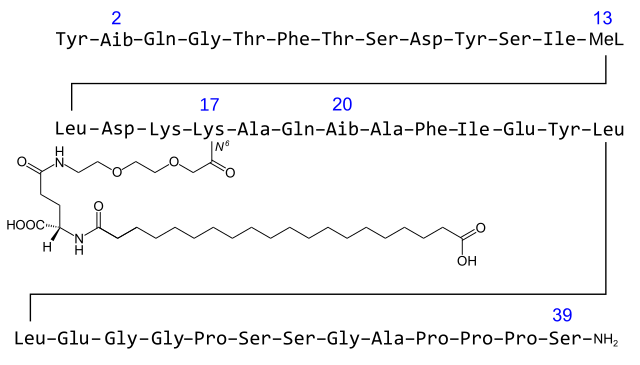
Retatrutide Peptide: A Multifaceted Tool in Metabolic and Cellular Research
Studies suggest that Retatrutide is an emerging peptide of considerable interest in the domain of metabolic research due to its complex pharmacological profile. Research indicates that with multiple functional properties, Retatrutide might offer a promising avenue for understanding metabolic processes, energy homeostasis, and various cellular mechanisms. This article explores the…
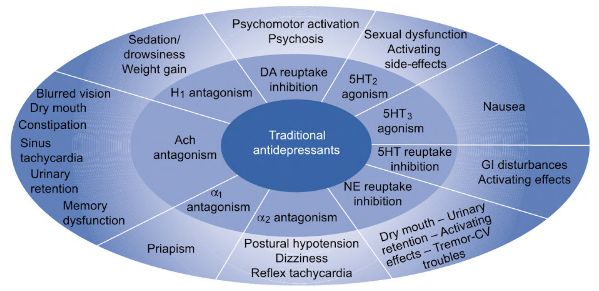
Antidepressants : Mnemonics
Classification and Mechanism of Action Acronyms: Mnemonic: TRIM 3N 3S Class Mechanism Drugs Side effects TCA Blocks reuptake of 5-HT, NA & other receptors (H1, ACh, α1, Voltage sensitive Na+ channel) Mnemonic: ANTI-DeP-C1. Amitryptiline, Amoxapine2. Nortryptiline3. Trimipramine4. Imipramine5. Doxepin, Desipramine, Dothiepin6. Protryptiline7. Clomipramine M1 blockade: Muscarinic anticholinergic side-effects α1 blockade:…
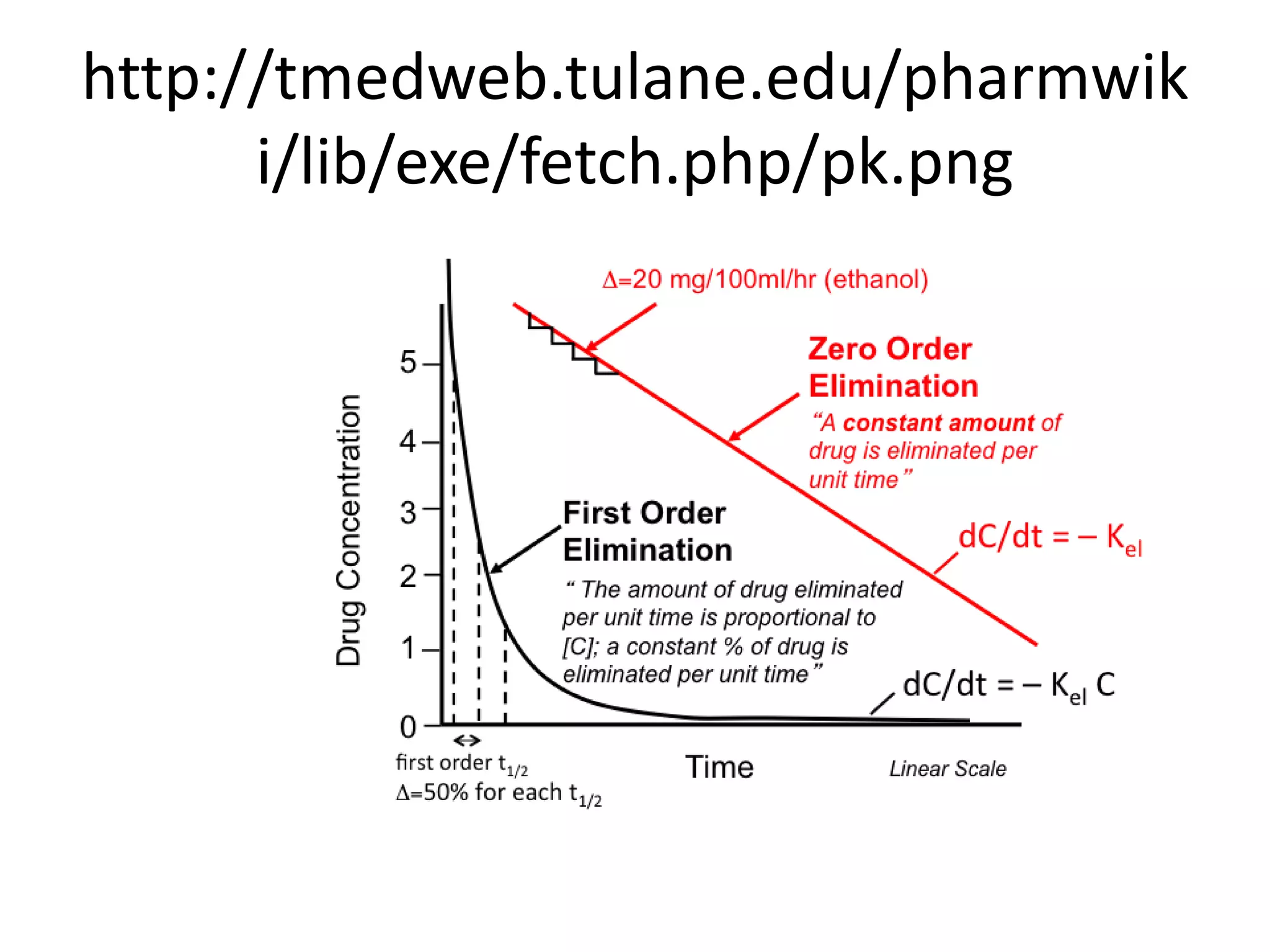
Drug Elimination Kinetics : Mnemonics
Zero-order First-order Amount of drug eliminated per unit time Constant amount Constant fraction (Mnemonic: first = fraction) Rate of elimination with plasma concentration Independent Directly proportional (greater the drug, greater is elimination) Elimination Capacity-limited, i.e. liver/kidney are saturated/maxed out on how much they can eliminate Flow-limited, i.e. liver/kidney are not…