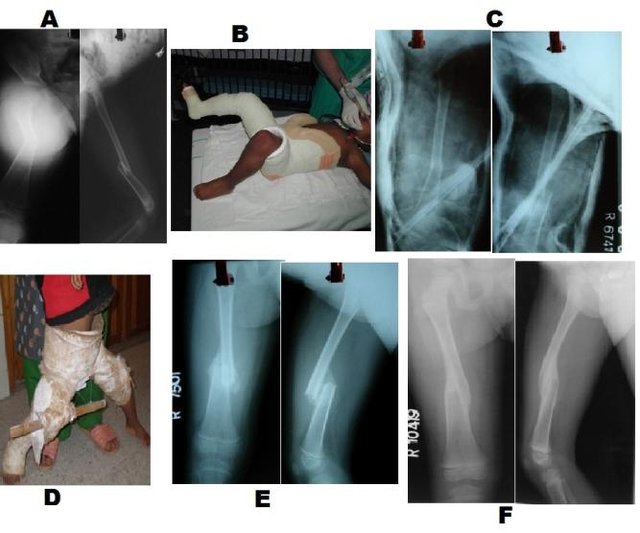
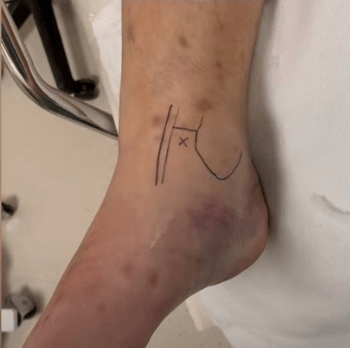1. A small stab incision is made on skin with a no. 11 Blade where the drain is anticipated.
2. A feeding tube of an appropriate size or IV set tube with side holes is placed through the skin incision site to the desired site.
3. The tube is fixed to the skin using a drain fixation technique.
4. The tube is clamped with hemostat or IV tube is clamped by rolling the roller clamp.
5. The hub of the drain is connected to the syringe of appropriate size (10 ml, 20 ml or 50 ml as per requirement) and the piston is pulled back against the clamped tube to create negative pressure.
6. To maintain a constant negative pressure, the plunger must be blocked from moving in. For this, 2 other syringe pistons/plunger or sheathed needles are placed between the barrel of syringe and the piston flange and taped to the piston.
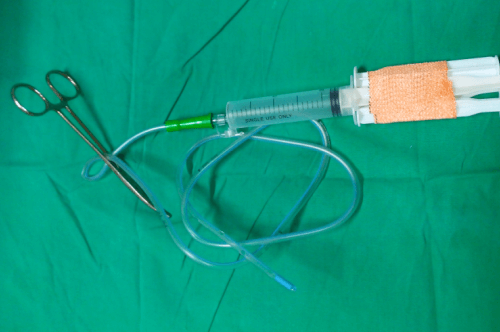
AS.
Syringe Suction Vacuum Drain: A Cheap Alternative. JPGO Volume 1 Issue 4, April 2014, available at: http://www.jpgo.org/2014/04/syringe-suction-vacuum-drain-cheap.html
Further reading:
1. Dwivedi JS, Gupta AS. Syringe Suction Vacuum Drain: A Cheap Alternative. JPGO Volume 1 Issue 4, April 2014, available at: http://www.jpgo.org/2014/04/syringe-suction-vacuum-drain-cheap.html
2. Mehrotra S, Mohanty SK, Maudar KK, Tyagi AK. SYRINGE SUCTION : A SIMPLE AND EFFECTIVE CLOSED DRAINAGE SYSTEM. Med J Armed Forces India. 1997 Oct;53(4):327-328. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(17)30777-3. Epub 2017 Jun 26. PMID: 28769534; PMCID: PMC5531143.
3. Venkatachalapathy TS, Nagendra Babu T, Sreeramulu PN (2012) A Simple Syringe Suction Drain for Surgical Procedures. J Clin Case Rep 2:216. doi:10.4172/2165-7920.1000216