Functions
Mnemonic: Six ‘C’s
- Contraction of muscles (Coupling of excitation-contraction)
- Conduction in nerves
- Cardiac function
- Coagulation in blood (Co-factor)
- Communication (intracellular messengers) for hormones, autacoids and transmitters
- Cementing (mineralization) of bone – Compressive strength
Distribution
Average young adult = 1200 gm calcium
- 99% in bone as calcium hydroxyapatite
- 1% in body fluids bone
- 1% in ECF
- 50% freely ionized (biologically active)
- 40% protein bound (80% to albumin and 20% to globulin)
- 10% complexed with small anions
- 99% in ICF
- 1% in ECF
Requirement
| Population | Requirement |
| Young children | 400-700 mg/day (2-3 dairy equivalents) |
| Adolescents and young adults (10-25 yrs) | 1300 mg/day (5 dairy equivalents) |
| Healthy adults (25-50 yrs) | 750 mg/day |
| Pregnant, Postmenopausal and Healing fracture | 1500 mg/day |
| Lactating | 2000 mg/day |
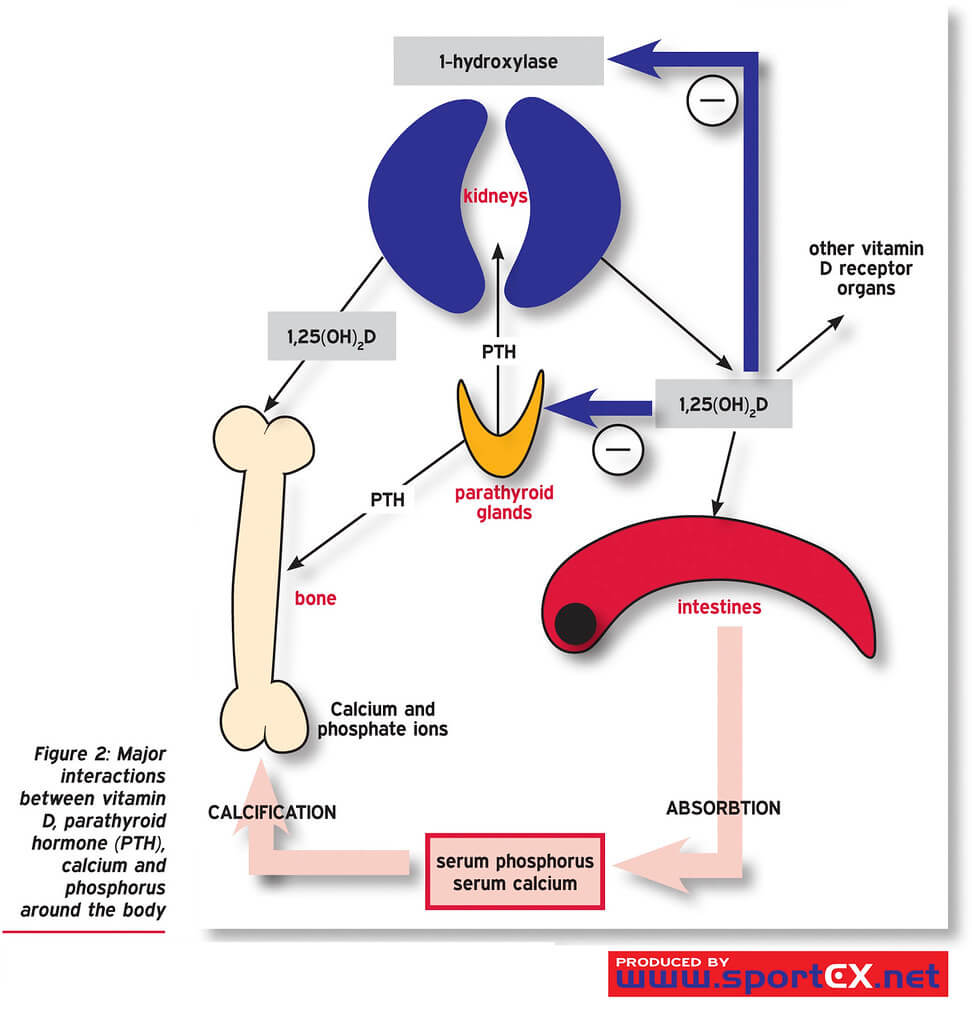
Metabolism
| Parathyroid hormone (PTH) | Vitamin D | Calcitonin | |
| Production | Parathyroid chief cells 🡢 PTH Negative feedback control by calcium | Diet/skin/UV 🡢 Vit. D3 Liver 🡢 25(OH) D Kidneys 🡢 1,25(OH)2 D | Thyroid parafollicular C cells 🡢 Calcitonin Positive feedback control by calcium |
| Intestine | 🡡 Calcium absorption 🡡 Phosphate absorption (Secondary PTH 🡢 Increased active vitamin D) | 🡡 Calcium absorption 🡡 Phosphate absorption | None |
| Kidney | 🡣 Calcium excretion (DCT) 🡡 Phosphate excretion 🡡 1,25 (OH)2 D production (1-α-hydroxylase) | 🡣 Calcium excretion 🡣 Phosphate excretion | 🡡Calcium excretion 🡡 Phosphate excretion |
| Bone | Binds to osteoblasts and upregulates RANKL 🡢 Activates osteoclasts 🡢 🡡 Calcium and phosphate resorption Pulsed = anabolic; Continuous = catabolic | 🡡 Calcium and Phosphate resorption [1,25(OH)2 D] 🡡 Bone formation [24,25(OD)2 D] | Inhibits osteoclasts 🡢 🡣 Calcium resorption |
| Net effect on serum levels | 🡡Calcium, 🡣Phosphate | 🡡Calcium, 🡡Phosphate | 🡣Calcium, 🡣Phosphate |
Mnemonics:
1. There’s 1 liver – 1st hydroxylation of vitamin D occurs in liver (makes calcidiol)
2. There are 2 kidneys – 2nd hydroxylation of vitamin D occurs in kidneys (makes calcitriol)
3. PTH = Phosphate Thrashing Hormone