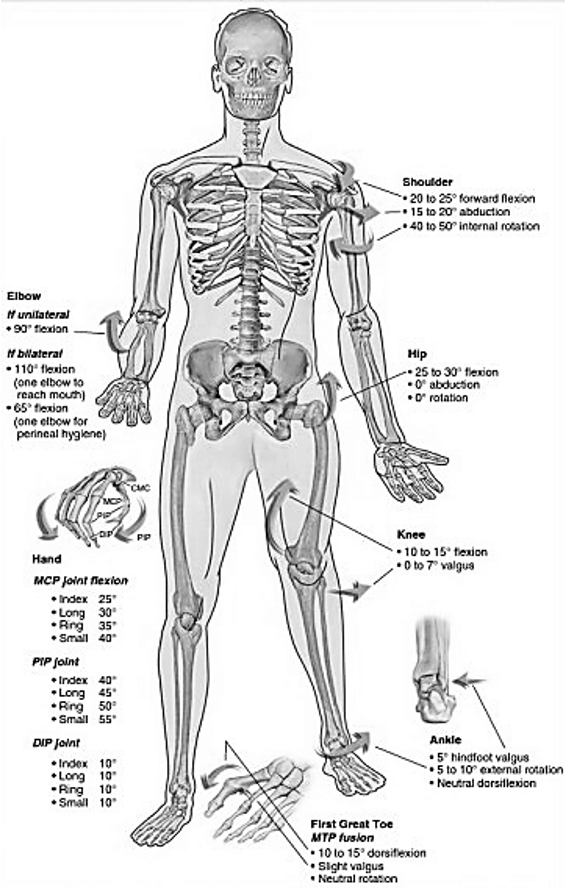
Arthrodesis is the surgical fusion of a diseased joint for the purposes of obtaining pain relief and stability. The bones are fused in a position permitting most useful function but lose their natural motion.
Shoulder
- Flexion: 30°
- Abduction: 20°
- Internal rotation: 40°
Elbow
- One side: 90°
- Both side: One in 110° (feeding) and another is 65° (perineal hygiene)
Wrist
- Non-rheumatoid: 10-20° dorsiflexion (power gripping) and neutral radio-ulnar deviation
- Rheumatoid: Neutral or flexed with 5-10° ulnar deviation (hygiene and perineal care are easier)
Hand
| Fingers | MCP | PIP | DIP |
| Index | 25 | 40 | 10 |
| Middle | 30 | 45 | 10 |
| Ring | 35 | 50 | 10 |
| Little | 40 | 55 | 10 |
Thumb
- CMC joint: 45° palmar abduction and 20° radial abduction (manual workers)/30-40° radial abduction (women)
- MCP joint: 10-20° flexion, 20° pronation, 20° abduction
- IP joint: 0-15° flexion
Hip
- Flexion: 25-30°
- Abduction: 0°
- Rotation: 0°
Knee
- Flexion: 10-15°
- Valgus: 0-7°
- External rotation: 10°
Ankle
- Hindfoot valgus: 5°
- External rotation: 5-10°
- Dorsiflexion: Neutral
- Talus: Posterior
If the ankle is fused in varus, the supinated foot becomes rigid and does not adapt to the ground during the second rocker phase. The lever arm of the foot becomes too long and impairs the third rocker phase if the talus is fused in an anterior position.
Subtalar
- Dorsiflexion: Neutral
- Heel valgus: 10°
Talonavicular
- Neutral dorsi/plantarflexion
Calcaneocuboid
- Heel valgus: 10°
- Forefoot ad/abduction and prono-supination: Neutral
Talonavicular joint should be fixed before calcaneocuboid joint during a triple arthrodesis.
1st great toe MTP
- Valgus: 15-20°
- Dorsiflexion: 10-15°
- Rotation: Neutral
Acronyms:
- CMC: Carpometacarpal
- MCP: Metacarpophalangeal
- PIP: Proximal interphalangeal
- DIP: Distal interphalangeal
- IP: Interphalangeal