Step 1: Rescuer 1 stabilizes head and neck in neutral position without applying traction. He/she should grasp the patient’s shoulders at the neck and gently position the patient’s head betweeen the forearms. Another rescuer should apply a semirigid extrication collar. Even with the collar in place, Rescuer 1 must maintain the head and neck in a neutral position until the log-rolling maneuver is complete.
Step 2: The patient is placed with his/her legs extended in the normal manner and her arms (palms inwards) extended by his/her sides. The patient will be rolled up on one arm with that arm providing proper spacing and acting as a splint for the body.
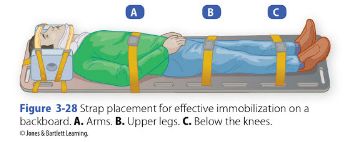
Step 3: The long blackboard is positioned next to the body. If one of the patient’s arms in injured, place the backboard on the injured side so that the patient will roll up on uninjured side.
Step 4: Rescuer 2 and 3 kneel at the patient’s side opposite the board. Rescuer 2 is positioned at the midchest area and Rescuer 3 is by the upper legs.
Step 5: With his knees, Rescuer 2 holds the patient’s near arm in place. He then reaches across the patient and grasps the shoulder and the hip, holding the patient’s far arm in place.
Step 6: With one hand, Rescuer 3 reaches across the patient and grasps the hip. With his other hand, he holds the feet together at the lower legs.
Step 7: When everyone is ready, Rescuer 1 (at the head end) gives the order to log-roll the patient.
Step 8: Rescuer 1 carefully maintains the head and neck in neutral position during the roll. Rescuer 2 and 3 roll the patient up on her side toward them. The patient’s arms are kept locked to her side to maintain a splinting effect. The head, shoulders and pelvis are kept in line during the roll.
Step 9: When the patient is on his/her side, Rescuer 2 (or Rescuer 4 if available) quickly examines the posterior surfae from occiput to heels for injuries.
Step 10: The backboard is now positioned next to the patient and held at a 30 to 45 degree angle by rescuer 2 and 3 (or rescuer 4 if available).
Step 11: When everybody is ready, Rescuer 1 gives the order to log-roll the patient onto the backboard. This is accomplished by keeping head, shoulders, and plevis in line.
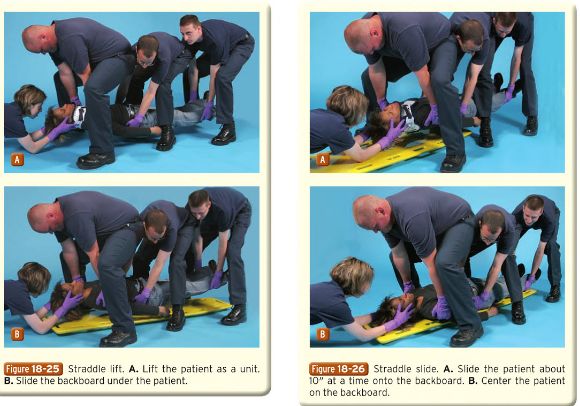
Use Straddle lift, if the space is not enough for performing log-roll maneuver.
Source:
International Trauma Life Support for Prehospital providers
Emergency Medical Responder: Your First Response in Emergency Care By David Schottke