International Surviving Sepsis Campaign has recommended Early Goal Directed Therapy for the management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Recently, three large multicenter studies – the ProCESS (Protocolized Care for Early Septic Shock), ARISE (Australasian Resuscitation In Sepsis Evaluation), and ProMISe (Protocolized Management In Sepsis) demonstrated no difference in the mortality in those receiving early goal directed therapy compared to the usual care group.
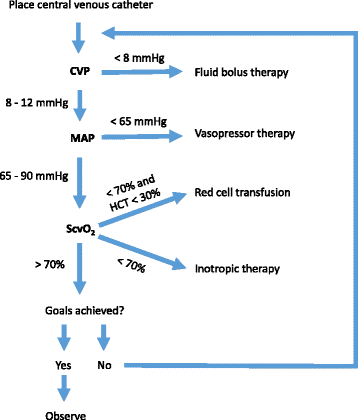
Early goal-directed therapy (EGDT) represents an attempt to predefine resuscitation end points to help clinicians at the bedside to resuscitate patients in septic shock.
Early goal-directed therapy (EGDT) proposed by Rivers et al. in 2001 1, a protocolized management of fluid replacement therapy in severe sepsis and septic shock resulted in a significant reduction in mortality (absolute risk reduction by 16%) as compared to the standard therapy. An identical protocol has been recommended by the International Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock.
Recently, three large studies the ProCESS 2, ARISE 3, and ProMISe 4 have challenged the benefit of this approach in improving survival in severe sepsis.
The mortality rate compared in the 4 trials in EGDT vs Usual care group are as follows:
- Rivers et.al.: 44.3% vs 56.9%
- ProCESS: 21% vs 18.9%
- ARISE: 18.6% vs 18.8%
- ProMISE: 29.5% vs 29.2%
Based on this unblinded, single centre study, EGDT soon became regarded as the “standard of care” around the world, and formed the basis of the 6-hour resuscitation bundle of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign. Several studies were published “claiming” that EGDT reduced mortality. These studies were used to support the notion that EGDT improved the outcome of patients’ with sepsis. However, the vast majority of these studies were retrospective, uncontrolled cohort studies where the investigators had vested interests in the outcomes of the studies.