The rotation of the hip must be assessed both with the hip in flexion and extension as well. In general, the range of motion for rotations are 5 to 10 degrees more in flexion compared to that in extension of hip.
If the range of motion for rotation varies between 2 positions by 20 degrees, it is considered as differential rotation. In the osteonecrosis of hip, there is positive differential rotation of hip in flexion compared to the extension which is called as sectoral sign. With the hip extended, internal rotation is almost full and with the hip flexed, the internal rotation is grossly restricted. This occurs due to sectoral involvement of the anterolateral part of femoral head in osteonecrosis or AVN of hip.
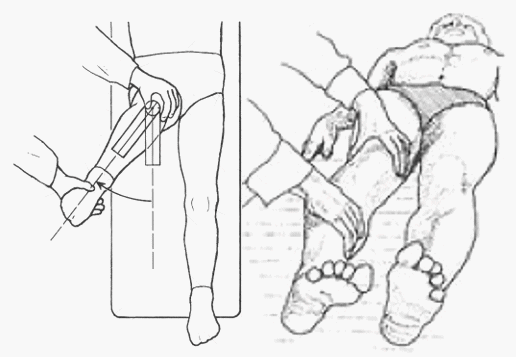
In cases of avascular necrosis (AVN) or osteonecrosis of hip, passive flexion of hip may lead to external rotation as well. This is called Catterall’s sign. Normally, when hip is flexed more than 90 degrees with flexed knee, the knee and patella faces towards the opposite shoulder, where as it faces the same axilla or shoulder, it should be considered positive axis deviation test. These tests correspond to the sectoral involvement of femoral head and sectoral sign.
References:
1. Musculoskeletal Examination By Vivek Pandey, Hitesh Shah
2. Apley’s System of Orthopaedics and Fractures edited by Louis Solomon, David Warwick, Selvadurai Nayagam
3. Osteonecrosis By Sudhir Babhulkar