Anatomy
Plantar fascia arise from medial and lateral tubercles on the inferior surface of calcaneus. The lesion is invariably found at the medial head.
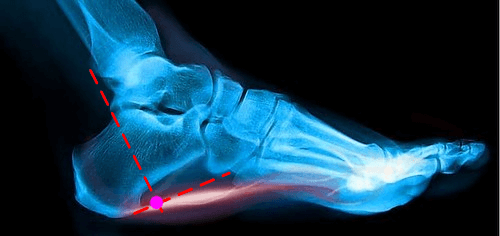
Intersection technique
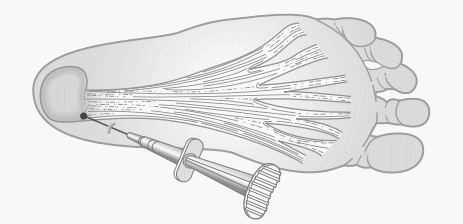
1. Position: Supine with knee flexed and hip externally rotated (figure of 4)
2. Landmark: Point of intersection of a line drawn parallel to axis of tibia from the posterior margin of medial malleolus and a horizontal line from inferior margin of medial calcaneal tuberosity
- The point of intersection is the proximal attachment of plantar fascia at the medial tubercle of calcaneal tuberosity
3. Medication: 1 ml of 40 mg/ml methylprednisolone + 1 ml of 10 mg/ml (1%) lignocaine + 3 ml normal saline (to enable wider diffusion) in 5 ml syringe with 18 G needle
4. Approach: At the intersection landmark, medial tubercle of calcaneal tuberosity is approached and advanced until deep plantar fascia is engaged. Inject the preparation of medication.
5. Post-injection: Injection site is covered with an adhesive coverlet
Reference: Salvi, A. E. (2015). Targeting the Plantar Fascia for Corticosteroid Injection. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 54(4), 683–685. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2014.10.011
Plantar approach
1. Position: Prone with foot held in strong dorsiflexion
2. Landmark: Identify tender point on medial side of heel
3. Medicine: 0.5 ml of 40 mg/ml Triamcinolone (20 mg) + 1.5 ml of 2% Lignocaine in 2 ml syringe with 21 G needle
4. Approach: Insert needle perpendicularly into medial side of soft part of sole, just distal to heel pad. Advance at 45 degrees towards calcaneus until touching bone. Pepper solution in 2 rows into fascia at its medial origin of bone.
Reference: Injection Techniques in Musculoskeletal Medicine – 5th Edition
Aftercare
1. Bilateral gel heel raises for men and low-heeled shoes for women
2. Intrinsic muscle exercise and daily active stretching of fascia
3. Rolling the foot on a golf ball or dense squash ball to apply deep friction can be helpful