Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterised by interruptions in breathing during sleep. Surprisingly, it’s a very common and often undiagnosed sleep disorder that affects many. While men and older individuals are particularly susceptible, sleep apnea often impacts even children, leading to behavioural issues and poor school performance.
There are several types of apnea with symptoms ranging from loud snoring to severe daytime fatigue. Untreated sleep apnea increases the risk of heart disease and is linked to hypertension, heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and daytime fatigue, significantly impacting one’s life quality.
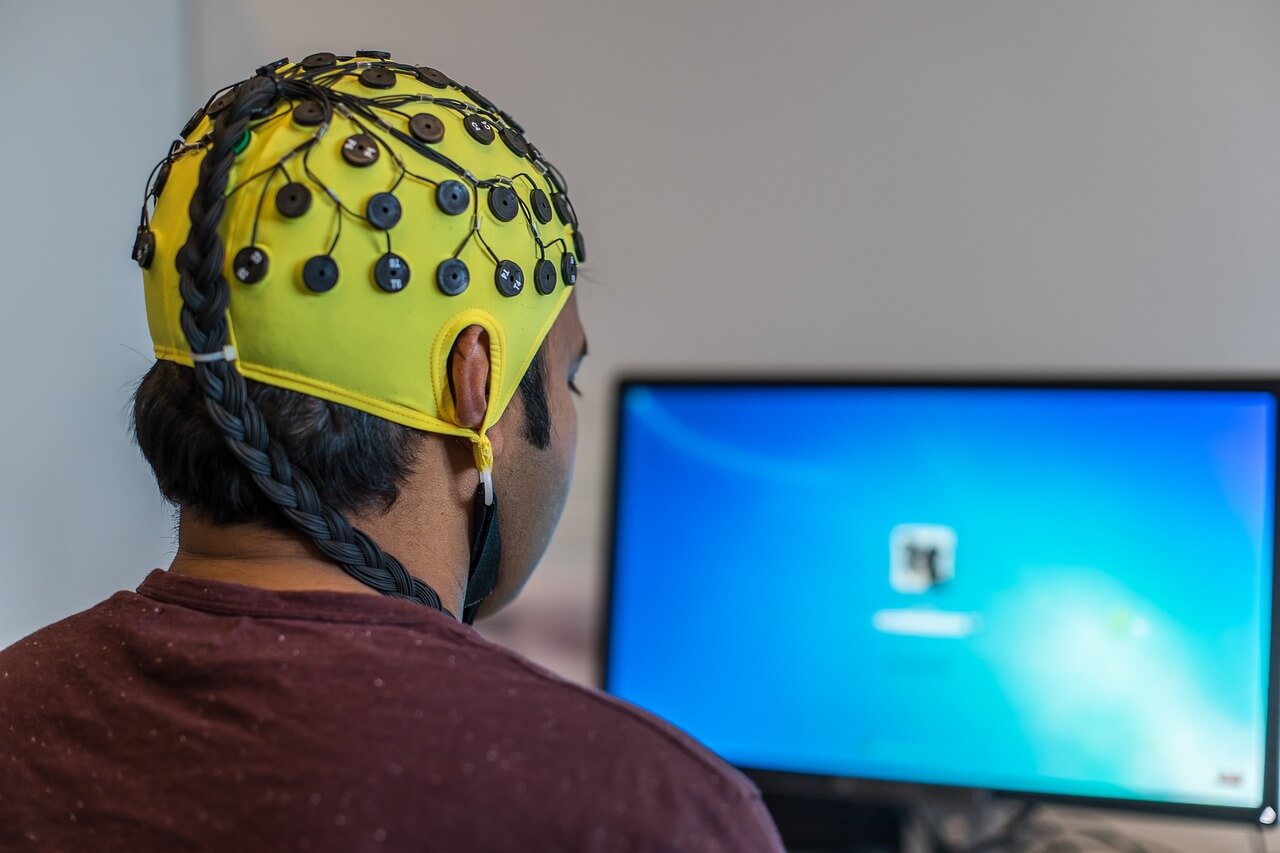
Recognizing the symptoms of sleep apnea is the first step towards diagnosis. Today, there are many tools one can use to understand the symptoms and get accurate diagnosis. One of them is taking a sleep apnea test as well as use of EEG (Electroencephalogram). As one of the tools used in the diagnostic process, EEG is used to measure the electrical activity of the brain and provides detailed insights into sleep patterns.

Source: Pexels
Introduction to EEG
By recording brain wave patterns, EEG helps identify disruptions in the sleep pattern that point to apnea events. During a sleep study, EEG sensors are placed on the scalp to monitor brain activity throughout the sleep cycles. More specifically, EEG measures the electrical activity of the brain by detecting voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current flows within the neurons of the brain. It provides a non-invasive way to monitor brain wave patterns, capturing data through electrodes placed on the scalp. This data is then represented as a series of waveforms that indicate various states of brain activity, such as wakefulness, relaxation, and different sleep stages. The primary brain waves detected arealpha, beta, delta, and theta waves, each of them associated with specific states of consciousness and sleep. This detailed brain activity monitoring allows doctors to identify abnormal brain wave patterns that could indicate neurological issues.
In medical diagnosis, EEG is also used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, brain tumours, head injuries, encephalitis, and other neurological disorders. In the context of sleep studies, EEG is an integral component of polysomnography (PSG), the comprehensive test used to diagnose sleep disorders. During a sleep study, EEG records brain activity throughout the various stages of sleep, helping to identify disruptions in sleep flow, such as frequent awakenings or abnormal sleep patterns. These disruptions are often associated with sleep apnea events, where breathing interruptions cause frequent waking up..
Source: Pixabay
Can EEG Alone Help the Detection of Sleep Apnea
EEG alone is insufficient to diagnose sleep apnea. Although sleep apnea involves repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, which can be detected through changes in brain wave patterns on an EEG, EEG does not measure the respiratory effort, airflow, or blood oxygen levels that are crucial for identifying the specific type and severity of sleep apnea.
So, the short answer is, while EEG can identify disruptions in sleep stages and frequent awakenings associated with sleep apnea, it cannot distinguish between the two different types of apnea. The first one is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), where the airway is physically blocked, and the second one is central sleep apnea (CSA), where the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Therefore, while EEG is an essential tool in the diagnostic process, it must be used in conjunction with other monitoring devices to accurately detect and diagnose all types of sleep apnea.
By analysing EEG data alongside other measurements, such as respiratory effort and oxygen levels, medical professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of a patient’s sleep health and accurately diagnose sleep apnea or other sleep-related issues and recommend the right treatment.

Source: Pixabay
Benefits and Limitations of Using EEG for Sleep Apnea Detection
As discussed above in the text, EEG provides valuable insights into sleep architecture and brain activity patterns associated with sleep apnea. However, its limitations include the inability to directly measure respiratory parameters critical for distinguishing between different types of sleep apnea. Still there are advantages and disadvantages of using it as a detection method.
Benefits of EEG
- Early Detection: EEG helps identify disruptions in sleep patterns and brain activity that indicate sleep apnea, enabling early intervention and treatment.
- Non-invasive Monitoring: EEG is a non-invasive procedure that involves placing electrodes on the scalp, making it comfortable and safe for patients during sleep studies.
- Objective Data: EEG provides objective data on brain wave activity, which helps clinicians assess the severity and impact of sleep apnea on cognitive function and overall brain health.
- Customised Treatment Plans: EEG data can help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans specific to the patient’s sleep patterns and apnea events, optimising therapeutic outcomes.
- Research Advancements: EEG data contributes to ongoing research in sleep medicine, improving understanding of sleep disorders and advancing treatment options for sleep apnea.
Limitations of EEG in Sleep Apnea Detection
- Direct Measurement of Breathing: EEG does not measure respiratory effort, airflow, or oxygen levels. These parameters are crucial for diagnosing the specific type of sleep apnea (obstructive, central, or mixed).
- Complementary Use: To diagnose sleep apnea accurately, EEG is used in conjunction with other tools in a comprehensive sleep study known as polysomnography (PSG). PSG includes additional sensors to monitor breathing, oxygen levels, and heart rate, providing a complete picture of the patient’s sleep health.
Conclusion
While EEG plays a crucial role in detecting disruptions during sleep, it is not sufficient on its own to diagnose all types of sleep apnea. Comprehensive sleep studies, including multiple diagnostic tools, are essential for accurately identifying and confirming the sleep apnea problem. Additionally, combinations of tool and detection processes are needed for the differentiating between obstructive, central, and mixed sleep apnea.



