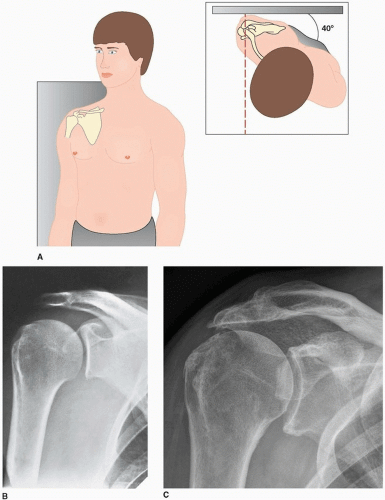
Shoulder X-ray views
AP Shoulder: in plane of thorax
AP in plane of scapula: Angled 45 degrees lateral
- Neutral rotation: Grashey view (estimation of glenohumeral space)
- Internal rotation/External rotation 30 degrees: Hill sach’s lesion and other humeral head morphology
Scapular Y lateral: Erect with opposite shoulder rotated 40 degrees out and beam centered on spine of scapula (shoulder dislocations and scapula fractures)
Supraspinatus outlet view: Scapular Y view with beam caudally tilted 10 degrees (Acromion morphology)
Axillary views:
- Standard axillary (Lawrence): Supine; arm abducted 90 degrees; beam inferior to superior, 15 to 30 degrees medial angulation depending on abduction
- West Point axillary: Prone; arm abducted 90 degrees and hanging over the table edge; beam angulated 25 degrees medially and anteriorly (detect Bankart fractures)
- Velpeau: Standing; wearing arm sling, leans backward over table 30 degrees; beam directed superior to inferior
- Trauma axillary lateral: Supine; arm supported in 20 degrees flexion by placing radiolucent material under elbow
Apical Oblique (Garth view): Grashey (True AP) view with beam 45 degrees caudally (to show anterior/inferior capsule; bony bankart/Hill Sachs)
Stryker-notch view: Supine; palm on head with elbow straight up; beam directed AP with 10 degrees cephalic aiming coracoid (Hill Sachs)
Zanca view: Erect; Beam centered on AC joint with 10 degrees cephalic tilt and 50% exposure (AC Joint)
Serendipity view: Supine; Beam centered on clavicle/manubrium with 40 degrees cephalic tilt (SC Joint)
Hobb’s view (90 degree cephalocaudal lateral): Sitting; Leans forward so that the anterior chest is in contact with film cassette & the flexed elbows straddle the cassette & support the patient; X-ray beam is directed directly down
For specific pathologies
a. Obligatory: AP, Lateral or axillary
b. Subacromial impingement: “Y” view
c. Coracoid impingement: Axillary, Lateral
d. Scapular pathology: “Y” view
e. Bankart: Garth view, West point view
f. Hill Sach’s: Stryker notch view, AP with Internal rotation
g. Glenohumeral arthritis: True AP in internal and external rotation and Axillary lateral view
h. Sternoclavicular pathology: Serendipity view, Hobb’s view
i. Acromioclavicular pathology: Zanca view; Stress view with 5 kg weight suspended on wrist and showing both shoulders