Murmur is a low, indistinct sound. In terms of medicine, it is the sound produced due to turbulent flow within the heart and great vessels. They are described and named in relation to the normal heart sounds, location, and quality.
Please go through these articles before reading further:
Mechanism of Murmur
Conditions where murmur may be heard:
- Pathological Heart Valve – Rheumatic Heart Disease, Degenerative Valves.
- Abnormal Communications of the Heart – Defects of Septum, PDA.
A heart murmur may always not be indicative of a structural abnormality. In situations causing hyper-dynamic circulation turbulence is created across the valves causing an INNOCENT MURMUR.
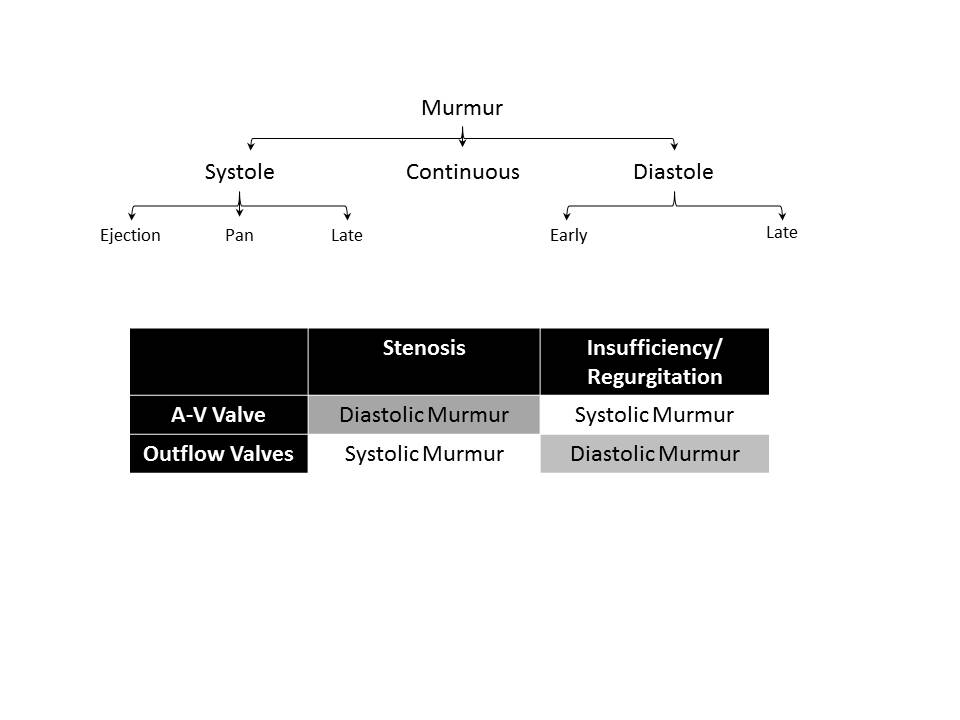
Murmurs
Location of the Murmur best heard: Towards the direction of the flow of blood. (In case of stenosis)
Valvular Heart Diseases and their Murmurs
Systolic Murmur
Diastolic Murmur
Continuous Murmur
Conclusion
- A systolic murmur from grade of 3/6 is considered significant.
- A diastolic murmur of any grade is significant and organic. (Diastolic Murmurs are graded into 4).
Summary
A murmur is the sound produced due to turbulent flow within the heart and great vessels. If within the heart, it may be due to degenerative valves or developmental defects.
Murmur can be classified into Systolic Murmurs, Diastolic Murmurs and Continuous Murmurs.
They are graded from 1 to 6 based on the intensity they produce and few additional characteristics.
Murmurs are not always constant in nature, but change during the phases of respiration and few manoeuvres.
References
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th Edition.
- Bates’ Guide to Physical Examination and History Taking, 10th Edition.
- Hutchinson’s Clinical Methods, 23rd Edition.
- First Aid for USMLE Step 1, 2019.
Graduated from one of the famous institutions in Telangana, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences. He has always been fond of writing articles in Medicine. Since the undergraduate years was interested in making creative Presentations and taking seminars.