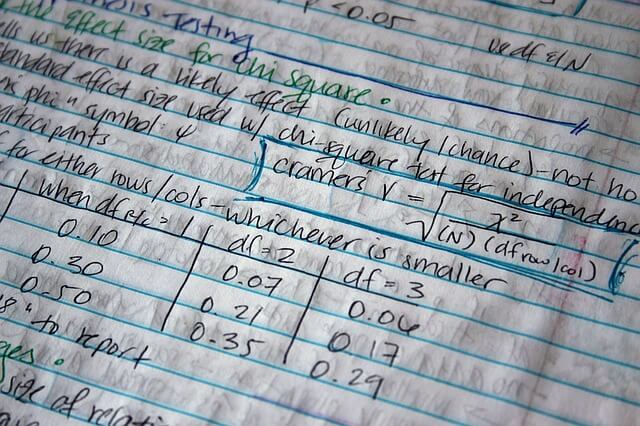Normal distribution
- Mean = Median = Mode
- 1 SD mean = 68.3% values
- 2 SD mean = 95.4% values
- 3 SD mean = 99.7% values
- Mean +/- 1.96 SD = 95% confidence interval
- SD = Square root (variance)
Non-normal distribution
a. Positive skew: Longer or fatter tail on right
- Mean > Median > Mode
b. Negative skew: Longer or fatter tail on left
- Mode > Median > Mean
2X2 tables
| Disease present | Disease absent | |
| Test positive | TP | FP |
| Test negative | FN | TN |
| Event | Non-event | |
| Exposed or Treatment | a | b |
| Non-exposed or Placebo | c | d |
Formulae
Incidence = No. of new cases in a given time/Total population at risk
Prevalence = No. of existing cases/Total population
Prevalence = Incidence X Duration
Case fatality rate = No. of death from a disease in given time/No. of cases in a given time
Sensitivity = True positive/Disease positive = TP/(TP+FN)
- Most acceptable screening tests are >80% sensitive
Specificity = True negative/Disease negative = TN/(TN+FP)
- Most acceptable confirmatory tests are >85% specific
False negative (FN) = 1 – Sensitivity
False positive (FP) = 1 – Specificity
Positive predictive value (PPV) = True positive/Test positive = TP/(TP + FP)
- Prevalence dependent (high prevalence = high PPV)
Negative predictive value (NPV) = True negative/Test negative = TN/(TN + FN)
- Prevalence dependent (low prevalence = high NPV)
Accuracy = (TP + TN)/(TP + FP + FN + TN)
Positive likelihood ratio = TP rate/FP rate = Sensitivity/(1-Specificity)
- Prevalence independent
Negative likelihood ratio = FN rate/TN rate = (1-Sensitivity)/Specificity
- Prevalence independent
Odds = Probability/(1-Probability)
Probability = Odds/(Odds + 1)
Pretest probability = Prevalence
Pretest odds = Pretest probability/(1-Pretest probability)
Post-test odds = Pre-test odds X Likelihood ratio
Post-test probability = Post-test odds/(1 + Post-test odds)
Posttest probability of positive test = PPV
Posttest probability of negative test = 1 – NPV
Relative risk (RR) = Experimental event rate/Control event rate = EER/CER = a/(a+b)/c/(c+d)
- Cohort study
- RR >1 = positive relationship between exposure and disease
- RR <1 = negative relationship between exposure and disease
- RR 1 = no relationship between exposure and disease
Attributable risk (AR) or Absolute risk reduction (ARR) = EER – CER = a/(a+b)/c/(c+d)
- AR = Rate of disease in exposed – Rate of disease in non-exposed
- ARR = Rate of disease in control group – Rate of disease in intervention group
Relative risk reduction = ARR/CER = (EER – CER)/CER
Numbers needed to treat (NNT) = 1/ARR
Numbers needed to harm (NNH) = 1/AR
Odds ratio = Odds of exposure in cases/Odds of exposure in controls = a/c/b/d = ad/bc
- Case-control study
Significance tests
Null hypothesis (H0) = No association exists between 2 selected variables (no difference between 2 treatments)
Alternate hypothesis (H1) = Association exists between 2 selected variables (difference exists between 2 treatments)
Type I error: Null hypothesis is rejected even though it is true (false positive)
- Not affected by sample size
- Increased if the number of end-points are increased
Type II error: Null hypothesis is not rejected even though it is false (false negative)
- Determined by both sample size and alpha
P-value (alpha): Probability of type I error
- Equals the significance level of a test
- If p <0.05, null hypothesis can be rejected (significant relationship exists between groups)
Beta: Probability of type II error
Power: 1 – Beta (i.e. probability of rejecting null hypothesis when it is false)
- Usually power of 0.8 is selected
- Increased sample size = Increased power
- Increased power = Decreased probability of type II error
Analyzing data
He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music.