Origin of Maxillary artery: Terminal branch of External Carotid Artery (ECA)
Derived from: 1st Arch
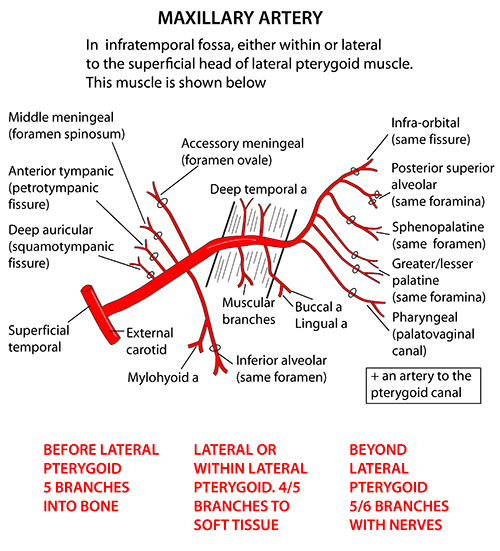
Divisions of Maxillary artery: 3 parts by lateral pterygoid
- 1st part (Mandibular part): winds around deep to neck of mandible
- 2nd part (Pterygoid part): travels between 2 heads of lateral pterygoid
- 3rd part (Pterygopalatine part): enters pterygopalatine fossa containing pterygopalatine galnglion
Branches of Maxillary artery
Remember:
- Each of the 3 divisions gives off 5 branches.
- Mandibular artery, i.e. Inferior alveolar artery is a branch of maxillary artery
- 2nd part: Branches supply muscles of mastication and do not cross through foramina in bones (all branches from 1st and 3rd part do cross)
Branches from 1st part
Mnemonic: Mandibular part gives off branches to 5 “M“s and the branches can be remembered as “DAMIA“
- Meatus (External auditory meatus) – Deep auricular
- Membrane (tympanic membrane) – Anterior tympanic
- Meninges and mater (duramater) – Medial meningeal
- Mandible – Inferior alveolar
- Meckel’s cave – Accessory meningeal
Clinical significance: Middle meningeal artery (MMA) injury results in Extradural hematoma (EDH). Auriculotemporal nerve wraps around it.
Branches from the 2nd part
Mnemonic: They supply muscles of mastication which are also derivatives of the 1st arch.
- Posterior deep temporal artery: Temporalis
- Pterygoid artery: Lateral and medial pterygoids
- Masseteric artery: Masseter
- Buccinator artery: Buccinator
- Anterior deep temporal artery: Temporalis
Branches from the 3rd part
Mnemonic: Remember the 5 “P“s
- Posterior superior alveolar artery: Maxilla
- Pterygoid canal artery: Upper part of pharynx and tympanic cavity
- Palatine – Descending palatine artery: Gives off greater and lesser palatine artery and supplies hard and soft palate respectively
- Palatine – Sphenopalatine or Nasopalatine artery: Nasal cavity
- Pharyngeal artery: Pharynx
There’s one more branch from the 3rd part, i.e. Infraorbital artery which gives off Anterior and Middle Superior Alveolar Artery.
Clinical significance: Sphenopalatine artery is a common cause of posterior epistaxis and may need ESPAL (Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation).