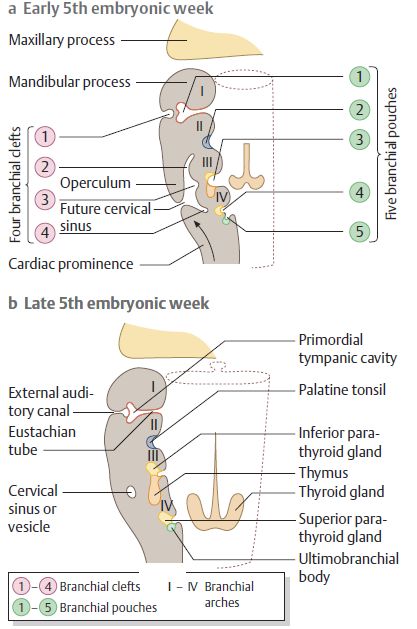
Synonym: Pharyngeal apparatus
Mnemonic: CAP covers from out to in
- Cleft: Ectoderm
- Arch: Mesoderm
- Pouch: Endoderm
Pharyngeal arches are equivalent of gill arches in fish that develop in a cranio-caudal sequence.
Derivatives of Pharyngeal or Branchial Apparatus
| Pharyngeal cleft | Pharyngeal arch | Pharyngeal pouch | ||||
| Ectoderm | Mesoderm | Neural crest | Cranial Nerves | Arteries | Endoderm | |
| 1st | External Auditory Meatus – epithelial lining | Mnemonic: MAT X 2 2 M: Mastication muscles, Mylohyoid 2 A: Anterior 2/3 tongue, Anterior belly of digastric 2 T: Tensor tympani, Tensor palatini Hillocks of His: 1 (Tragus), 2 (helical crus) and 3 (helix) | Mnemonic: M’s 1. Meckle’s cartilage 2. Mandible 3. spheno-Mandibular ligaments 4. Middle ear bones (Malleus and Incus) | CN V3 (Mandibular division of Trigeminal nerve) | Maxillary artery | Auditory tube, Middle ear cavity and inner layer of tympanic membrane epithelial lining |
| Also known as Mandibular arch. | ||||||
| 2nd | Obliterated | Mnemonic: S Smiling (muslces of facial expression) Stapedius, Stylohyoid, poSterior belly of digastric muscle Hillocks of His: 4 (antihelix crus), 5 (scapha), 6 (lobule) | Reichert’s cartilage: Stapes Styloid Stylohyoid ligament leSSer horn of hyoid | CN VII/seven (Facial nerve) | Stapedial artery | Tonisllar fossa and Crypts of palatine tonsil |
| Also known as Hyoid arch. | ||||||
| 3rd | Obliterated | Stylopharyngeus, Superior and middle constrictors of pharynx | Greater horn and lower body of hyoid | CN IX (Glossopharyngeal nerve) | Common and Internal carotid arteries | Inferior parathyroid gland and Thymus |
| 4th | Obliterated | Muscles of soft palate (except tensor veli palatini) Muscles of the pharynx (except stylopharyngeus) Cricothyroid, Inferior pharyngeal constrictor (Cricopharyngeus), Laryngeal Cartilages (thyroid and cuneiform) | None | CN X – Superior laryngeal nerve | Aorta (left) and Subclavian artery (right) | Parafollicular “C” cells of thyroid (Neural crest cell migration into ultimobranchial body) and Superior parathyroid gland |
| 5th | Absent | Absent | Absent | |||
| 6th | Absent | Laryngeal cartilages (Cricoid, arytenoid, corniculate), Intrinsic muscles of larynx (except cricothyroid), Upper muscles of esophagus | None | CN X – Recurrent laryngeal nerve | Ductus arteriosus and pulmonary artery | Absent |
Clinical Correlate
1. First Arch Syndrome:
- Cause: Lack of migration of neural crest cells into pharyngeal arch I
- Defect: Defective development of facial bones
- Example: Treacher-Collins syndrome (mandibulofacial dysostosis), Pierre-Robin syndrome
2. Branchial Cyst Fistula:
- Cause: Persistence of 2nd pharyngeal cleft/groove and 2nd pharyngeal pouch
- Defect: Patent opening from internal tonsillar area, passes between internal and external carotid arteries and exits to skin anterior to sternocleidomastoid
3. Cervical sinus:
- Cause: Persistence of pharyngeal grooves 2-4
- Defect: Cyst anterior to the border of sternocleidomastoid
4. Digeorge syndrome:
- Cause: Failure of differentiation of 3rd and 4th pharyngeal arch
- Defect: Absent parathyroid glands (hypocalcemia), thymus (T cell immunodeficiency), Facial abnormalities similar to first arch syndrome
CATCH-22 Syndrome: Cardiac abnormalities, Abnormal facies, Thymic aplasia, Cleft palate, Hypocalcemia – from deletion of chomosome 22
5. Complex innervation pattern of tongue:
Tongue receives contributions from pharyngeal arches 1-4:
Anterior 2/3 (oral part) of tongue:
- Forms from the median tongue bud and two distal tongue buds that develop in the floor of the pharynx associated with pharyngeal arch 1.
- The distal tongue buds overgrow the median tongue bud and fuse in the midline, forming the median sulcus.
- General sensation: Lingual branch of CN V3
- Taste: Chorda tympani branch of CN VII
Posterior 1/3 (pharyngeal part) of tongue:
- Forms from the copula and hypobranchial eminence that develop in the floor of the pharynx associated with pharyngeal arches 2–4.
- The hypobranchial eminence overgrows the copula, thereby eliminating any contribution of pharyngeal arch 2 in the formation of the definitive adult tongue.
- General sensation and taste: both from 3rd pharyngeal arch (CN IX)
Motor: Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of tongue develop from occipital somites.
- Motor innervation is through CN XII except palatoglossus which is innervated by CN X.
6. Development of Ear:
- Branchial arch 1: Hillocks of His 1-3, Malleus, Incus, Tensor tympani (dampens sound)
- Branchial arch 2: Hillocks of His 4-6, Stapes, Stapedius muscle (dampens sound)
- Pharyngeal pouch 1: Middle ear cavity, Eustachian tube
- Pharyngeal cleft 1: External auditory meatus
- Branchial membrane 1 (between pouch and cleft): Tympanic membrane
7. Persistent stapedial artery:
The stapedial artery is transiently present in normal fetal development, connecting the branches of the future external carotid artery (ECA) to the internal carotid artery (ICA). Postembryonic persistence of the stapedial artery is rare. The stapedial artery may present as a pulsatile middle ear mass or may be found incidentally during middle ear surgery.
8. Preauricular sinus:
- Cause: Abnormalities in the fusion of Hillocks of His
- Defect: Pit like depression anterior to the crus of helix
9. Thyroid descent: The thyroid gland arises from between the first and second arch as a diverticulum (thyroglossal duct) which grows downwards leaving the foramen caecum at its origin. Incomplete thyroid descent may give rise to a lingual thyroid, a thyroglossal duct cyst or a pyramidal thyroid lobe. If the thyroid gland descends too far, it may result in a retrosternal goitre.