What investigations to order for synovial fluid sample?
Mnemonic: 5 Cs
- Chemistry (pH, LDH, glucose, protein)
- Cell counts
- Cytology
- Culture
- Crystals
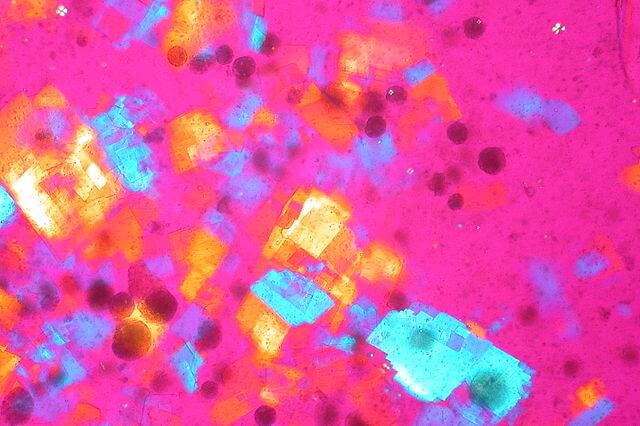
Ed Uthman, MD, pathologist, Houston, Texas, USA / CC BY
Interpretation of synovial fluid analysis
| Gross | Normal | Non-inflammatory | Inflammatory | Septic | Crystal | Hemorrhagic |
| Volume (ml) | <3.5 | >3.5 | >3.5 | >3.5 | >3.5 | >3.5 |
| Viscosity | High | High | Low | Variable | Variable | Variable |
| Color | Colorless to straw | Straw to yellow | Yellow Cloudy | Yellow-white Cloudy | Yellow Cloudy | Red Xanthochromic |
| Routine lab | ||||||
| WBC | <200 | 200-2000 | 2000-75000 | Often >100000 | 2000-75000 | 50-10000 |
| PMN (%) | <25 | <25 | >50 | >75 | >50 | <50 |
| Crystals | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Positive | Negative |
| Mucin clot | Firm | Firm | Friable | Friable | Friable | |
| Glucose (AM fasting) | Nearly equal to blood | Nearly equal to blood | <50 mg% lower than blood | >50 mg% lower than blood | >50 mg% lower than blood | Nearly equal to blood |
| Examples | OA, Trauma, AVN, SLE | RA, Reiter’s, SLE, Viral, Fungal, TB | Bacterial | Gout, Pseudogout | Trauma, fracture, ligament tear, hemophilia, charcot arthritis, PVN |
Crystals in Gout and Pseudogout
Mnemonic: “P” for Pseudogout
Pseudogout:
- Polarized microscopy
- Positive birefrengence
- Pyrophosphate crystals
- Polygon (Rhomboid) shaped
- Purple (blue) color
Gout:
- Negative birefrengence
- Needle shaped
- Urate crystals
- Yellow color
Mnemonic: Look for ABC (Alignment, Blue, Calcium) in crystal analysis. If the crystal aligned with the red-plate compensator is blue, it is calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate. Urate crystals are the opposite, being yellow when parallel to the compensator.
References:
1. Clinical Laboratory Medicine edited by Kenneth D. McClatchey
2. Rheumatology Secrets By Sterling G. West