Definition: Breathlessness inappropriate to the level of physical exertion or even occurring at rest (subjective and not a sign)
Mechanisms:
Chemoreceptors:
Peripheral: Carotid and aortic bodies (to pO2, pCO2 and H+)
Central: Medulla (to pCO2, not pO2, change in pH of CSF)
a. Increased work of breathing:
- Airflow obstruction: Bronchial asthma, COPD, Tracheal obstruction
- Decreased pulmonary compliance: Pulmonary edema, fibrosis, allergic alveolitis
- Restricted chest expansion: Ankylosing spondylitis, Respiratory paralysis, Kyphoscoliosis
b. Increased ventilatory drive:
- Increased physiological deadspace (V/Q mismatch): Consolidation, Collapse, PE, Pulmonary edema
- Hyperventilation due to receptor stimulation:
- Chemoreceptors: Acidosis, Hypoxia (Shock, Pneumonia), Hypercapnia
- J receptors at alveolo-capillary junction: Pulmonary edema, Pulmonary embolism, Pulmonary congestion (Activates Hering-Breur reflex which terminates inspiratory effort before full inspiration is achieved – rapid and shallow)
- Muscle spindles in intercostal muscles: Tension-length disparity
- Central: Exertion, anxiety, thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma
c. Impaired respiratory muscle function: Polio, GBS, Myasthenia
Corollary discharge: When the CNS voluntarily sends a signal to the respiratory muscles to increase the work of breathing, it also sends a copy to the sensory cortex telling it there is an increased work of breathing.
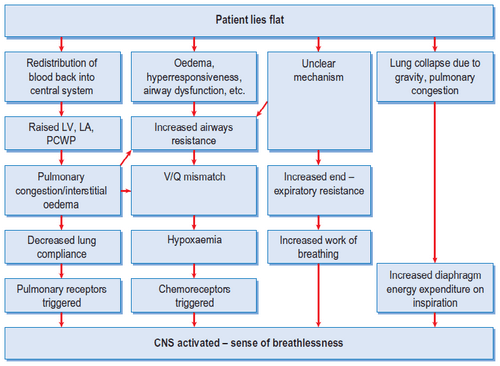
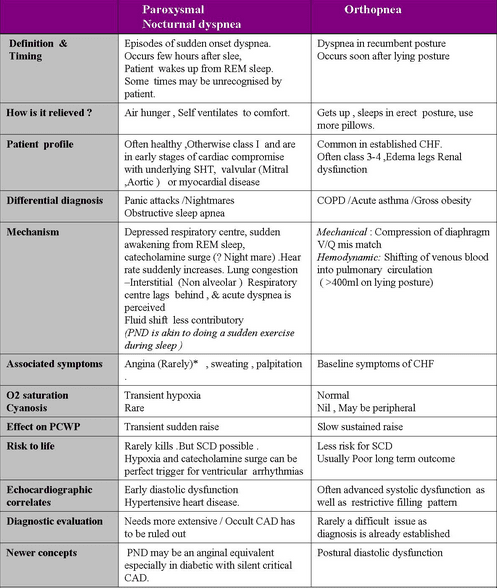
Orthopnea:
- Pulmonary congestion during recumbency (cannot be pumped out of LV) seen in CHF, COPD and Asthma
- Increased venous return
- Diaphragm elevation leading to decreased vital capacity
Dyspnea in COPD:
- Hypoxia and hypercapnia: Chemoreceptors
- Increased airway resistance and hyperinflation
- Deconditioning: Reduced threshold at which respiratory muscles produce lactic acidosis
Basics: A normal 70 kg person breathes 12-15/min with a tidal volume of 600 ml. A normal individual is not aware of respiratory effort until ventilation is doubled, and dyspnea is not experienced until ventilation is tripled.
Paraoxysmal nocturnal dyspnea: Decreased responsiveness of respiratory center in brain and decreased adrenergic activity in myocardium during sleep and pulmonary congestion 2-5 hours after onset of sleep
- Takes 10-30 min for recovery after upright posture
Trepopnea: Dyspnea worse when lying on one side and relieved by lying on opposite side
Causes:
- Unilateral lung disease: Good lung receives more blood supply due to gravity
- CHF: Lying on right side enhances venous return and sympathetic activity
- Lung tumor: Gravity induced compression of blood vessels or lung
Platypnea: Dyspnea on sitting or standing and relieved by supine position
Causes:
- Venous to arterial shunting (Lung bases)
- Intra-cardiac shunts (ASD, Pneumonectomy)
- Intrapulmonary Rt to Lt shunt (Hepatopulmonary syndrome, PE, COPD)
- ARDS
Platypnea in Hepatopulmonary syndrome:
- Diffuse intrapulmonary shunts
- Impaired hypoxic vasoconstriction (V/Q mismatch)
- Pleural effusion and diaphragmatic dysfunction
- Hyperdynamic circulation and low pulmonary resistance
Features:
a. Onset and Duration: Can ask when able to run upstairs?
- Minutes to hours (Rapid onset): Pneumothorax, Acute asthma, PE, Pulmonary edema, Foreign Body
- Hours to days (Gradual onset): Pneumonia, Pleural effusion, Anemia, GBS
- Months to years (Slow onset): PTB, COPD, Carcinoma, Fibrosing alveolitis
b. Severity: How far before stopping? How any flights of stairs? At rest? Sleep? Talking? Dressing?
MRC grading:
- I – On sternous exertion
- II – Hurrying on level ground or Walking up slight hill
- III – Walks slower than people of same age or Stops when walking at own pace on level
- IV – Stops after 100 yards (90 m) or after few minutes in level
- V – Breathless to leave house, dress or undress
NYHA classification of severity of heart failure:
- I – No limitation with ordinary physical activity
- II – Mild limitation of ordinary physical activity
- III – Marked limitation of activity, symptoms with exertion
- IV – Symptoms at rest
c. Aggravating and relieving factors:
- Improves on weekend/holidays: Occupational asthma, extrinsic allergic alveolitis
- Recumbency/Sleep: Orthopnea/PND
d. Associated symptoms:
- Pleuritic chest pain: Pneumonia, Pulmonary infarction, Rib fracture, Pneumothorax
- Central non-pleuritic chest pain: MI, Massive PE
- Cough or wheeze: Asthma, PE, Pneumothorax