Pleura is a mesothelial lined sac that envelopes the lungs and comprises of 2 membranous walls i.e. visceral pleura and parietal pleura that encloses pleural space filled with pleural fluid. Pleural space contains about 0.3 ml/kg body weight of pleural fluid. The pleura is not visible on a normal CXR except where it forms part of a lung fissure or where the two lungs abut each other in the midline
Erect frontal Chest X-ray:
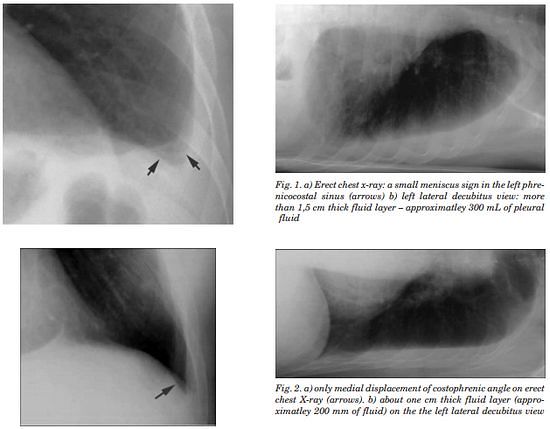
- Obliteration of costophrenic angle: requires 200-300 ml pleural fluid
- Concave meniscus (horizontal in case of hydropneumothorax)
- Massive pleural effusion: opacification of entire hemithorax and shifting of mediastinum to the opposite side
- Causes “white-out” lung
- Around 5-7 l of pleural fluid
- Lamellar pleural effusion: linear opacification paralleling the lateral aspect of lung
- Encysted pleural effusion: loculation within a fissure or elsewhere
- Can be mistaken for lung tumor
- Subpulmonic effusion:
- left: widening of the distance between gastric bubble and the superior margin of hemidiaphragm (normally < 7mm)
- right: peak of the hemidiaphragm is shifted laterally
Lateral Chest X-ray:
Lateral films are able to identify a smaller amount of fluid as the costophrenic angles are deepest posteriorly
- Can detect an effusion as small as 50 ml
Supine Chest X-ray:
Due to the effect of gravity, the pleural fluid is distributed throughout the posterior part of the pleural during supine position – this cause the hemithorax to appear whiter or paler grey compared to the normal side. Vessels are often visible through the shadowing.
- Requires about 200 ml fluid