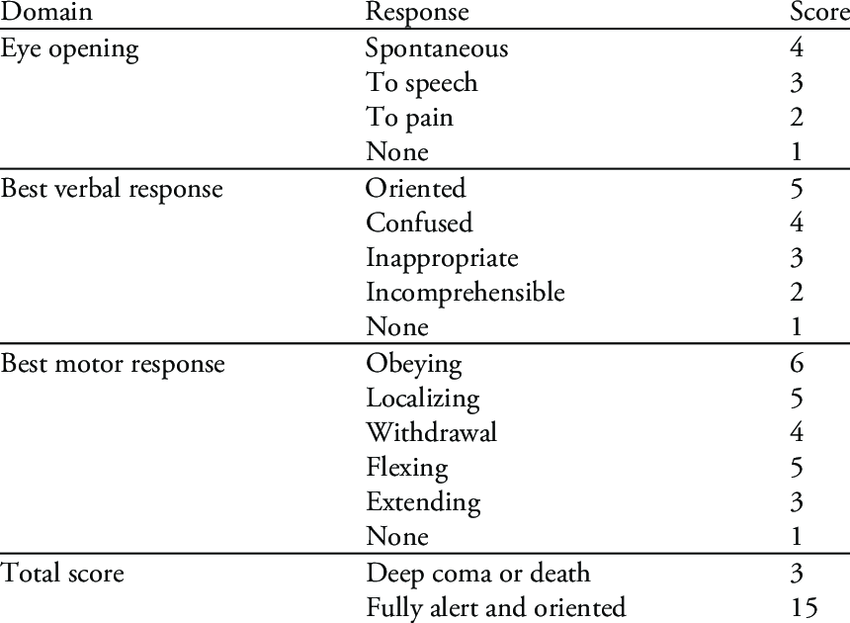
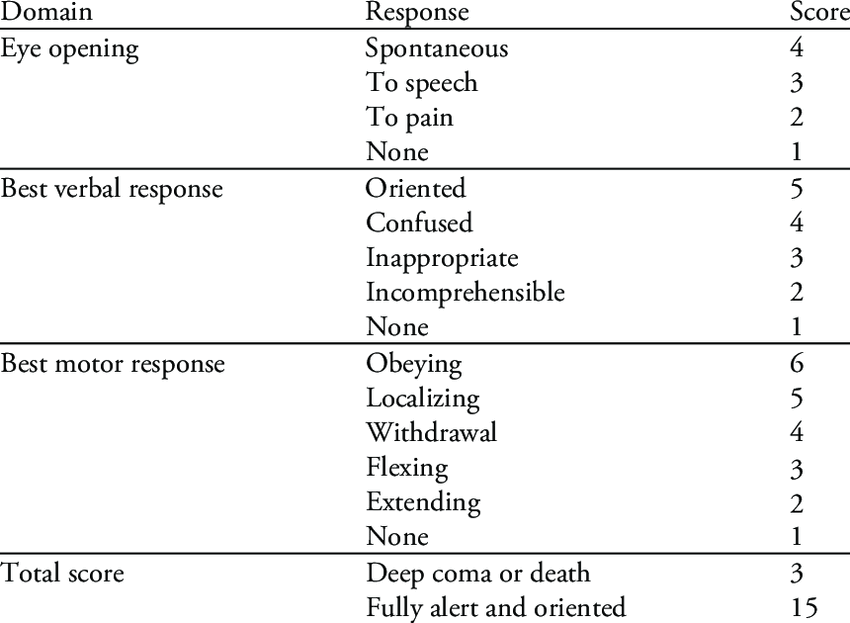
Best eye opening
Mnemonic: ESPN
- 4 – Eye(s) open spontaneously
- 3 – to Sounds
- 2 – to Pain
- 1 – No opening
Best verbal response
Mnemonic: ASWGN
- 5 – Appropriate
- 4 – Sentences (confused)
- 3 – Words (inappropriate)
- 2 – Groans and grunts (incomprehensible)
- 1 – No sound
Best motor response
Mnemonic: OLD BEN
- 6 – Obeys
- 5 – Localizes pain
- 4 – Draws away from pain (withdrawal)
- 3 – Bends to pain, i.e., decorticate
- 2 – Extends to pain, i.e., decerebrate (extends elbow to nailbed pressure)
- 1 – No response
Important points
- Minimum score = 3
- Maximum score = 15 or 11T (if intubated)
- Record best response in each category and sum of all 3. e.g., E3 V3 M4 (10)
- “1T” is designated in verbal response for intubated patients. e.g., E3 V1T M4 (8T)
- GCS ≤ 8 = Coma
- GCS < 8 = Intubate (If less than eight, intubate)
- Head injury classification:
- Mild: GCS 13-15
- Moderate: GCS 9-12
- Severe: GCS 3-8
- ICP monitoring indications:
- GCS ≤ 8 after resuscitation + abnormal head CT scan
- GCS ≤ 8 + normal head CT scan + ≥2 risk factors for intracranial hypertension (including age >40 years, SBP < 90 mmHg, and motor posturing)
- CT head indications:
- GCS <15 at 2 hours following injury
- GCS <13 at any stage
Question and Example
A 20 year old man is hit over the head with a mallet. On arrival in the accident and emergency department he opens his eyes to pain and groans or grunts. On application of a painful stimulus to his hands, he extends his arm at the elbow. What is his Glasgow coma score?
- E = Pain (2)
- V = Groans/grunts (2)
- M = Extends to pain (2)
So, his GCS is E2 V2 M2 (6).