Neonatal reflexes are the reflexes which are present at birth and have a predictable course of appearance and disappearance. A normally developing newborn should respond to certain stimuli with these reflexes, which eventually become inhibited as the child matures.
The list of reflexes that can be elicited in normal newborn are:
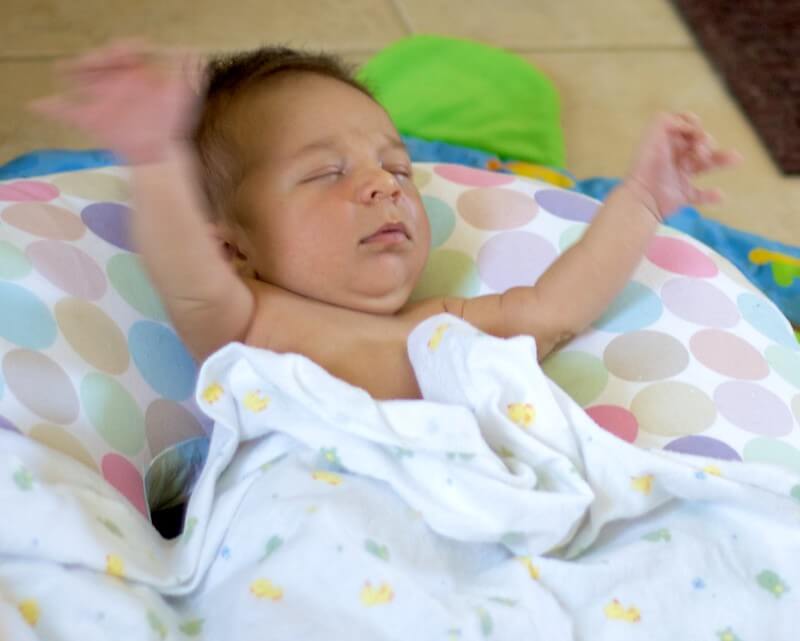
- Moros Reflex
- Rooting reflex
- Sucking reflex
- Grasp reflex
- Babinski reflex
- Asymmetric tonic neck reflex (ATNR)
- Gallant reflex
- Stepping reflex
- Landau’s reflex
- Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex
| Reflex | Stimulation | Response | Duration |
| Babinski | Sole of foot stroked | Fans out toes and twists foot in | Disappears at 9 months – 1 year |
| Blinking | Flash of light or puff of air | Closes eyes | Permanent |
| Grasping | Palms touched | Grasps tightly | Weakens at 3 months; disappears at 1 year |
| Moro | Sudden move; loud noise | Startles; throws out arms and legs and then pulls them toward body | Disappears at 3-4 months |
| Rooting | Cheek stroked or side of mouth touched | Turns toward source, opens mouth and sucks | Disappears at 3-4 months |
| Stepping | Infant held upright with feet touching ground | Moves feet as if to walk | Disappears at 3-4 months |
| Sucking | Mouth touched by object | Sucks on object | Disappears at 3-4 months |
| Swimming | Placed face down in water | Makes coordinated swimming movements | Disappears at 6-7 months |
| Tonic neck | Placed on back | Makes fists and turns head to the right | Disappears at 2 months |
After going through the table, you can now watch this video showing the commonly elicited neonatal reflexes and their significance.
Here is a helpful library on Pediatric neurology.

MD Pediatrics and Fellowship Neonatology, he chooses to stay anonymous. He often writes his views online as well as share few important topics for medical students, doctors and specially parents. He does research in pediatrics.